|
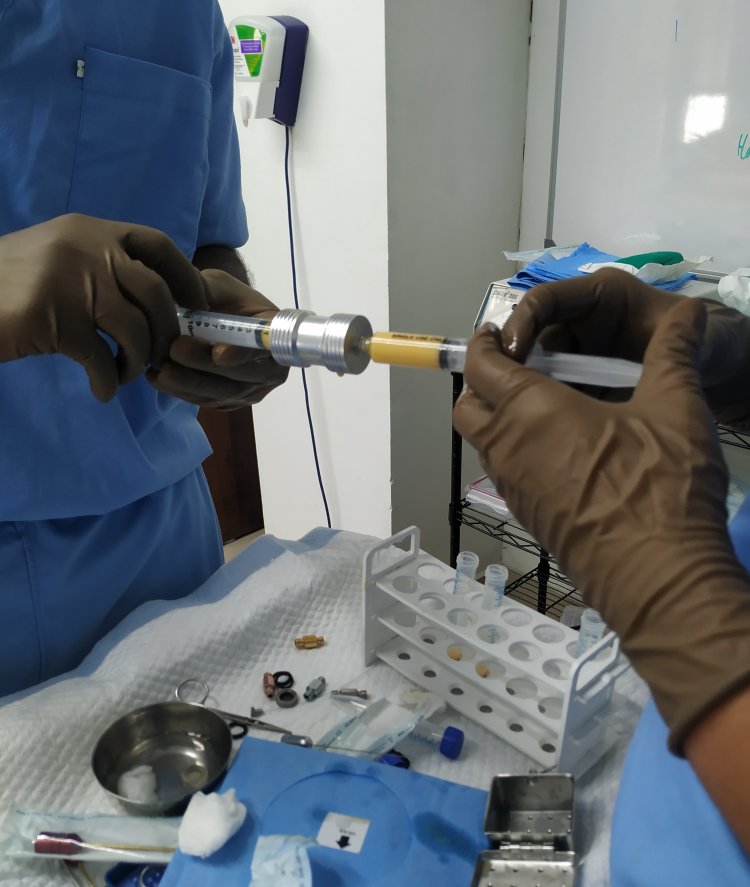
Emulsified fat grafting is an innovative technique that may help individuals experiencing hair loss. This minimally invasive procedure involves taking fat from the patient's own body, processing it, and then carefully injecting it into the scalp.
The process starts by gently extracting fat from an area like the abdomen or thighs using a small, thin cannula. The harvested fat is then prepared for reinjection. The prepared fat is then injected into the scalp using fine needles, targeting the areas affected by hair loss. One key advantage of emulsified fat grafting is the potential for longer-lasting results compared to other treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections. The injected fat can help stimulate new hair follicle growth and improve blood flow to the scalp, potentially leading to better hair density and thickness. Emulsified fat grafting is typically an outpatient procedure, meaning the patient can go home the same day. Recovery time is generally minimal, with little to no downtime reported by patients. The video in Malayalam gives an overview of the topic.
0 Comments
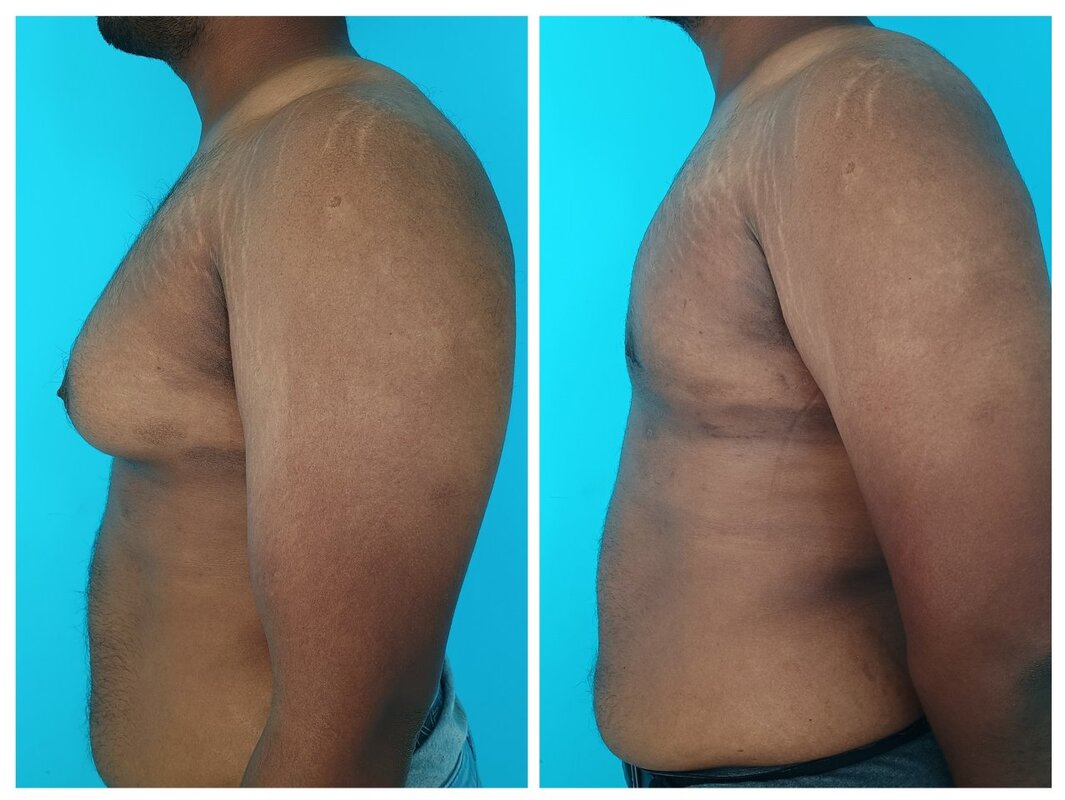
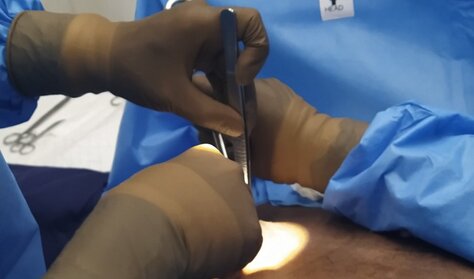
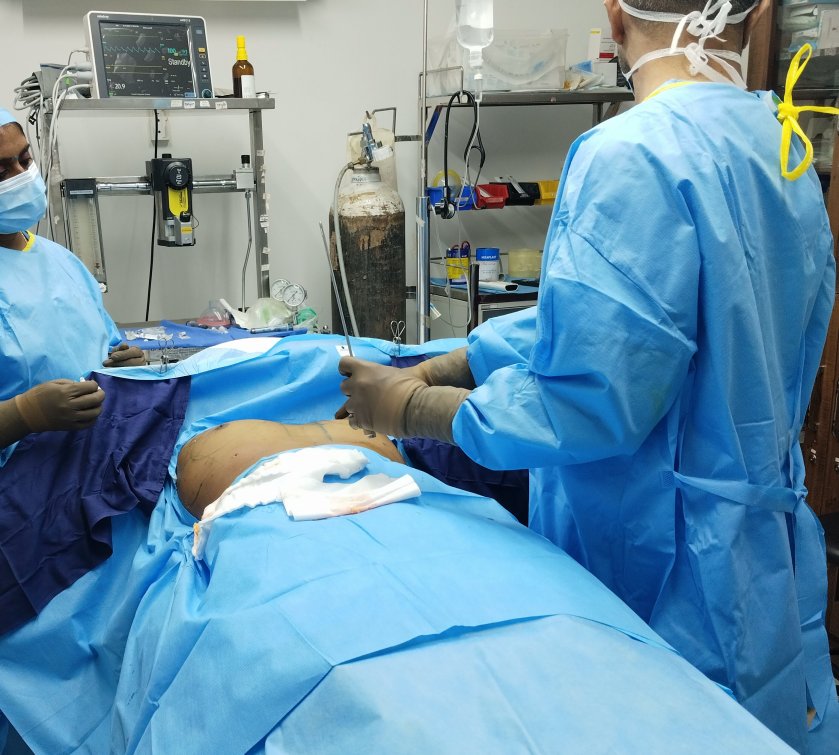
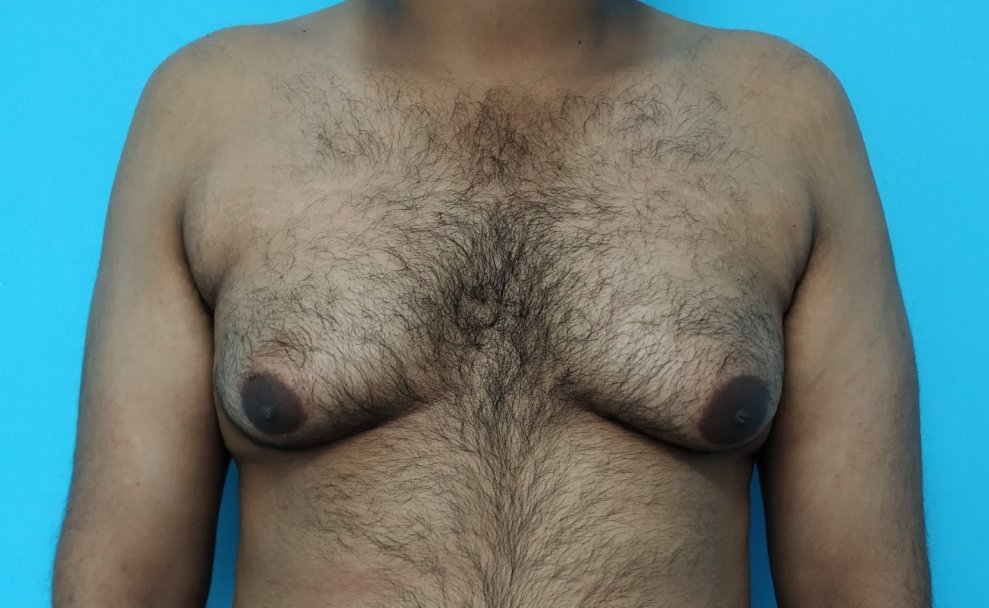
Gynecomastia, or enlarged male breasts, is a common condition that we treat in our medical practice. Many patients express concerns about potential complications from gynecomastia surgery. However, it's important to note that gynecomastia surgery is generally a safe procedure, and complications are uncommon. The risk of complications can be further lowered by addressing modifiable risk factors. This video discusses the various aspects that can help patients avoid complications from gynecomastia surgery. Some key points covered in the video include: - Proper patient selection and evaluation - Surgical techniques to minimize tissue trauma - Strategies to manage postoperative swelling and bleeding - Importance of following postoperative care instructions By understanding these factors, patients can feel more confident about the safety and outcomes of gynecomastia surgery. The video provides a comprehensive overview to help address common concerns and ensure the best possible results for our patients. 1. Why do gynecomastia surgery?
Gynecomastia correction is done to improve the appearance. This helps in reducing the sense of shame and discomfort with the appearance. 2. What are the steps for undergoing gynecomastia correction?
3. What is the cost of the procedure? Would there be additional costs? The cost of the procedure depends on the anesthesia (local vs general), and the deformity (extent of liposuction and need for skin resection). In most patients, the surgical cost of liposuction and gland excision comes to approximately 70,000 rupees. The additional costs include stay and investigations. These may cost you an additional 5000 rupees. 4. Are there any EMI schemes? We do not offer any loan or EMI scheme. We do not encourage individuals to take loans for procedures. In case of any financial difficulties, you could talk to one of us. 5. Which anesthesia is used for correction? Most of our procedures are done under local anesthesia. General anesthesia is usually done for anxious individuals or those who require skin resection (removal). Modern anesthesia protocols are safe. 6. Which surgical procedure is carried out for gynecomastia correction? The steps depend on the deformity. In most of our patients we do the following:
7. What is the recovery following gynecomastia correction? Most patients have an uneventful recovery. We recommend the following:
8. I stay far away. Can I come directly for surgery? We do not encourage combining consultation and procedure at one visit. We believe an individual needs additional time to understand the procedure, possible outcomes, and complications. We also require investigation reports to rule out any other issues. Hence we advise a separate visit for the consultation before the procedure. 9.Can I come to the surgery alone? No. We want you to be accompanied by a close relative or a dependable friend. This is for the following reasons,
10. I'm staying abroad. I want to get it done during my vacation. Are there any additional steps that I should take? We advise the following to such individuals:
11. Are there any risks to life? Modern anaesthesia protocols are very safe. So any serious complications are very unlikely. 12. Will I get a recurrence? Most patients do not get a recurrence. Individuals who are prone to recurrence are those below 18 years of age and secondary gynecomastia. For more information please click here. 1.എന്തുകൊണ്ടാണ് ഗൈനക്കോമാസ്റ്റിയ ശസ്ത്രക്രിയ നടത്തുന്നത്? കാഴ്ച മെച്ചപ്പെടുത്താൻ ഗൈനക്കോമാസ്റ്റിയ ശസ്ത്രക്രിയ നടത്തുന്നു. ഇത് കാഴ്ചയിൽ നാണക്കേടും അസ്വസ്ഥതയും കുറയ്ക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്നു. 2. ഗൈനക്കോമാസ്റ്റിയ ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയ്ക്ക് വിധേയമാക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള ഘട്ടങ്ങൾ എന്തൊക്കെയാണ്? 1. കൺസൾട്ടേഷൻ: ഞങ്ങൾ നിങ്ങളെ പരിശോധിക്കുന്നു. ക്ലിനിക്കൽ കണ്ടെത്തലുകളെ അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കി ഒരു ചികിത്സാ പദ്ധതി ഞങ്ങൾ നിർദ്ദേശിക്കുന്നു. 2. ലാബ് പരിശോധനകൾ. അവയിൽ ഹോർമോണുകളുടെ അളവ് സംബന്ധിച്ച പരിശോധനകൾ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു.ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയ്ക്കുള്ള ഫിറ്റ്നസ് വിലയിരുത്തുന്നതിന് മറ്റ് പരിശോധനകൾ നടത്തുന്നു. നിങ്ങളുടെ വീടിനടുത്തുള്ള ലാബിൽ ഇവ ചെയ്യാവുന്നതാണ്. 3. നടപടിക്രമം: ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയെത്തുടർന്ന് ആശുപത്രിയിൽ രാത്രി താമസമുണ്ട്. മറ്റൊരു ജില്ലയിലേക്ക് യാത്ര ചെയ്യേണ്ടി വരുന്ന രോഗികൾ ഒരു ദിവസം കൂടി താമസിക്കണം. 4. തുടർ സന്ദർശനങ്ങൾ: ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയുടെ അടുത്ത ദിവസം ഡ്രെയിനുകൾ നീക്കം ചെയ്യുകയും ഡ്രെസ്സിംഗുകൾ മാറ്റുകയും ചെയ്യും. നിങ്ങൾ വീട്ടിലെത്തിക്കഴിഞ്ഞാൽ ആദ്യത്തെ ഫോളോ അപ്പ് 2 ആഴ്ചയ്ക്ക് ശേഷമാണ്. പിന്നീടുള്ള സന്ദർശനങ്ങൾ 1 മാസം, 3 മാസം, 6 മാസങ്ങളിലാണ്. 3. ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയുടെ ചെലവ് എത്രയാണ്? അധിക ചിലവുകൾ ഉണ്ടാകുമോ? ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയുടെ ചെലവ് അനസ്തേഷ്യ (ലോക്കൽ vs ജനറൽ), വൈകല്യം (ലിപ്പോസക്ഷൻ്റെ വ്യാപ്തിയും ത്വക്ക് വിഭജനത്തിൻ്റെ ആവശ്യകതയും) എന്നിവയെ ആശ്രയിച്ചിരിക്കുന്നു. മിക്ക രോഗികളിലും ലിപ്പോസക്ഷൻ്റെയും ഗ്ലാൻ എക്സിഷൻ്റെയും ശസ്ത്രക്രിയാ ചെലവ് ഏകദേശം 70,000 രൂപ വരും. അധിക ചെലവുകളിൽ താമസവും ലാബ് അന്വേഷണവും ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു. ഇവയ്ക്ക് നിങ്ങൾക്ക് 5000 രൂപ അധികമായി ചിലവായേക്കാം. 4. എന്തെങ്കിലും EMI സ്കീമുകൾ ഉണ്ടോ? ഞങ്ങൾ ഒരു ലോണും EMI സ്കീമും വാഗ്ദാനം ചെയ്യുന്നില്ല. നടപടിക്രമങ്ങൾക്കായി വായ്പ എടുക്കുന്നതിൽ നിന്ന് ഞങ്ങൾ വ്യക്തികളെ പ്രോത്സാഹിപ്പിക്കുന്നില്ല. എന്തെങ്കിലും സാമ്പത്തിക ബുദ്ധിമുട്ടുകൾ ഉണ്ടെങ്കിൽ ഞങ്ങളിൽ ഒരാളോട് സംസാരിക്കാം. 5. ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയ്ക്ക് ഏത് അനസ്തേഷ്യയാണ് ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നത്? ഞങ്ങളുടെ മിക്ക നടപടിക്രമങ്ങളും ലോക്കൽ അനസ്തേഷ്യയിലാണ് ചെയ്യുന്നത്. ഉത്കണ്ഠയുള്ള വ്യക്തികൾക്കോ ചർമ്മം നീക്കം ചെയ്യേണ്ടവർക്കോ സാധാരണയായി ജനറൽ അനസ്തേഷ്യ ചെയ്യാറുണ്ട്. ആധുനിക അനസ്തേഷ്യ പ്രോട്ടോക്കോളുകൾ സുരക്ഷിതമാണ്. 6. ഗൈനക്കോമാസ്റ്റിയയ്ക്ക് ഏത് തരത്തിലുള്ള ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയാണ് നടത്തുന്നത്? ഞങ്ങളുടെ മിക്ക രോഗികളിലും ഞങ്ങൾ ഇനിപ്പറയുന്നവ ചെയ്യുന്നു: 1.ലിപ്പോസക്ഷൻ. കൊഴുപ്പ് നീക്കം ചെയ്യുന്നതിനാണ് ഇത് ചെയ്യുന്നത്. ഇത് മികച്ച രൂപം ലഭിക്കാനും നടപടിക്രമം സുരക്ഷിതമാക്കാനും സഹായിക്കുന്നു. 2.ഗ്രന്ഥി നീക്കം ചെയ്യൽ. ഏരിയോളയിൽ (മുലക്കണ്ണിന് ചുറ്റുമുള്ള ചർമ്മം) ഒരു ചെറിയ മുറിവിൻ്റെ സഹായത്തോടെയാണ് ഇത് ചെയ്യുന്നത്. ഞങ്ങളുടെ മിക്ക രോഗികളിലും ഞങ്ങൾ ചർമ്മം നീക്കം ചെയ്യുന്നില്ല. 7. ഗൈനക്കോമാസ്റ്റിയ ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയ്ക്ക് ശേഷം എനിക്ക് എപ്പോഴാണ് ജോലിയിലേക്ക് മടങ്ങാൻ കഴിയുക? ഇനിപ്പറയുന്നവ ഞങ്ങൾ ശുപാർശ ചെയ്യുന്നു:
8. ഞാൻ ദൂരെയാണ് താമസിക്കുന്നത്. എനിക്ക് ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയ്ക്ക് നേരിട്ട് വരാമോ? ഒരു സന്ദർശനത്തിൽ കൺസൾട്ടേഷനും ശസ്ത്രക്രിയയും സംയോജിപ്പിക്കുന്നത് ഞങ്ങൾ പ്രോത്സാഹിപ്പിക്കുന്നില്ല. ശസ്ത്രക്രിയ, ഫലങ്ങൾ, സങ്കീർണതകൾ എന്നിവ മനസ്സിലാക്കാൻ ഒരു വ്യക്തിക്ക് കൂടുതൽ സമയം ആവശ്യമാണെന്ന് ഞങ്ങൾ വിശ്വസിക്കുന്നു. മറ്റേതെങ്കിലും പ്രശ്നങ്ങൾ ഒഴിവാക്കുന്നതിന് ഞങ്ങൾക്ക് ലബോറട്ടറി അന്വേഷണ റിപ്പോർട്ടുകളും ആവശ്യമാണ്. അതിനാൽ, നടപടിക്രമത്തിന് മുമ്പ് കൂടിയാലോചനയ്ക്കായി ഒരു പ്രത്യേക സന്ദർശനം ഞങ്ങൾ നിർദ്ദേശിക്കുന്നു. 9. എനിക്ക് ഒറ്റയ്ക്ക് സർജറിക്ക് വരാമോ? ഇല്ല. നിങ്ങളോടൊപ്പം ഒരു അടുത്ത ബന്ധുവോ സുഹൃത്തോ ഉണ്ടായിരിക്കണമെന്ന് ഞങ്ങൾ ആവശ്യപ്പെടുന്നു. ഇത് ഇനിപ്പറയുന്ന കാരണങ്ങളാലാണ്, ചില വ്യക്തികൾക്ക് ശസ്ത്രക്രിയാനന്തര കാലഘട്ടത്തിൽ സഹായം ആവശ്യമായി വന്നേക്കാം. നടപടിക്രമത്തെക്കുറിച്ചും ചികിത്സാ പദ്ധതിയിലെ എന്തെങ്കിലും മാറ്റങ്ങളെക്കുറിച്ചും ഒരു വ്യക്തി ബോധവാനായിരിക്കണമെന്ന് ഞങ്ങൾ ആവശ്യപ്പെടുന്നു. ഒരാൾ കൂടെയുണ്ടെങ്കിൽ അത് മാനസികാരോഗ്യത്തിന് സഹായിക്കുന്നു. 10. ഞാൻ വിദേശത്താണ് താമസം. എൻ്റെ അവധിക്കാലത്ത് അത് പൂർത്തിയാക്കാൻ ഞാൻ ആഗ്രഹിക്കുന്നു. ഞാൻ എന്തെങ്കിലും അധിക നടപടികൾ സ്വീകരിക്കേണ്ടതുണ്ടോ? അത്തരം വ്യക്തികൾക്ക് ഞങ്ങൾ ഇനിപ്പറയുന്നവ ഉപദേശിക്കുന്നു:
11. ജീവന് എന്തെങ്കിലും അപകടങ്ങൾ ഉണ്ടോ? ആധുനിക അനസ്തേഷ്യ പ്രോട്ടോക്കോളുകൾ വളരെ സുരക്ഷിതമാണ്. അതിനാൽ, ഗുരുതരമായ സങ്കീർണതകൾ ഉണ്ടാകാനുള്ള സാധ്യത വളരെ കുറവാണ്. 12. എനിക്ക് ഗൈനക്കോമാസ്റ്റിയ വീണ്ടും വരുമോ? മിക്ക രോഗികൾക്കും ഗൈനക്കോമാസ്റ്റിയയുടെ ആവർത്തനം ലഭിക്കുന്നില്ല. 18 വയസ്സിന് താഴെയുള്ളവരും ദ്വിതീയ ഗൈനക്കോമാസ്റ്റിയയുമാണ് ആവർത്തനത്തിന് സാധ്യതയുള്ള വ്യക്തികൾ. കൂടുതൽ വിവരങ്ങൾക്ക് ദയവായി ഇവിടെ സന്ദർശിക്കുക In our practice we frequently come across concerns about the pain associated with gynecomastia surgery both during and after the procedure. Thoughts about the pain can lead to a lot of anxiety in those affected by this condition. It may even prevent some individuals from seeking treatment.
Pain is subjective. Pain is a protective sensation that helps animals avoid injury. Postoperative pain is due to the stimulation of the nerve endings at the operated site. The use of pain medications help reduce the discomfort. Modifications in the surgical technique can contribute to less pain. Gynecomastia surgery is a short stay procedure. Patients can go home without a prolonged inpatient stay. This is made possible due to adequate pain relief with oral medicines. There are a few reasons for less pain following a gynecomastia correction whn compared to other surgical procedures. These include,
Most patients do not require more than oral medications for postoperative comfort. This is more so among individuals treated under local anaesthesia. Local anaesthesia helps identify nerve sparing and address it before the completion of the procedure. Nerve sparing my occur when the procedure is performed under general anesthesia. Fear about pain can discourage many from getting surgery. But the improvements in anaesthesia and newer surgical technique, lead to a comfortable postoperative period in most individuals. They usually do not require more than a few oral pain medicines in the initial few days following surgery. To learn more about gynecomastia, click here. Liposuction is a part of the treatment of gynecomastia correction in most of our patients. It is relatively uncommon to do a gynecomastia correction without accompanying liposuction. Why so?
Liposuction has many advantages. They include the following:
There are instances when we may not do liposuction during gynecomastia surgery. But these are relatively uncommon. Liposuction is sometimes not done in thin individuals with less breast fat. Such individuals usually present with a gland enlargement confined to the area under the areola. They also have a very thin skin pinch. In such situations, we proceed with a gland excision through an areolar incision after local anesthetic infiltration. Liposuction has many benefits when done in gynecomastia treatment. It is usually done in almost all cases of gynecomastia surgery in our practice. To learn more about gynecomastia, please click here. Gynecomastia is excess breast tissue in men. In a subset of individuals with gynecomastia, there can be redundant or excess skin. The excess skin affects the outcomes following a gynecomastia corrective surgery. It can mean a longer duration to achieve an acceptable outcome. In some cases, we may do additional surgery to take care of excess skin.
How does skin redundancy present in gynecomastia? Redundant skin is usually apparent with a clinical examination. The breast tissue tends to sag in such individuals. The breasts appear deflated. There can be visible folds on the lower part, and lateral areas of the chest. The presence of ptosis or sagging gives an aged appearance to the chest. Who are the individuals prone to get skin redundancy associated with gynecomastia? The risk factors associated with excess skin in gynecomastia include:
What are the treatment strategies that can be adopted in case of skin excess? hereAmong individuals with excess body weight, it is always recommended to lose weight before undergoing a surgical correction. Optimizing the body weight before surgery has certain advantages. It is easier to assess the extent of excess skin before surgery. This makes the surgical outcome more predictable. In some cases, we may opt to undertake skin reduction during the time of gynecomastia correction. With weight loss, patients can benefit from the skin recoil beforehand. In an individual, with excess skin, gynecomastia correction can be done in two different ways. It can be done either with skin excision or without skin excess. Both strategies lead to different outcomes. When the correction is carried out without a skin excision there may be a postoperative course with an increase in the deflated appearance. This usually improves with time due to the skin recoil. It may take many months before the full extent of skin recoil is appreciated. We usually advise our patients to wait as much as 8 months before deciding on an additional surgery to remove the skin excess. Many patients are usually satisfied with the skin recoil and choose not to have any skin excision procedures. This has the advantage of an initial simpler procedure with shorter scars. Skin excisional procedures are associated with longer and more visible scars. The second strategy would include gynecomastia correction carried out with simultaneous skin excision. The pattern of the excision can vary depending on the extent of skin excess. Patients with more excess tend to have a greater amount of skin removed. With this technique, the excess skin is addressed in a single procedure. However, it carries the disadvantage of longer scars. In our practice, this approach is less commonly used. We tend to choose individuals with severe excess for this approach. What are the steps that can be taken by an individual to address excess skin? The excess skin is usually seen to accompany increased body weight. Individuals should try to maintain their weight close to ideal. This is usually achieved with the help of dietary modifications such as diet and exercise. Weight training helps recruit the excess skin and contributes to reduced sagging over the lower part of the chest. Weight training and accompanying muscle hypertrophy also bring along aesthetic benefits. Excess skin is seen in some individuals presenting with gynecomastia. This is more commonly seen in those with excess body weight. The skin excess can be tackled with surgery in a staged or simultaneous way. Both strategies have their advantages and disadvantages. A treatment plan is chosen based on individual preferences and extent of excess skin. Individuals with skin excess can help improve this condition with appropriate dietary modifications and exercise. Learn more about gynecomastia here. Smoking and plastic surgery
Smoking is bad for plastic surgery. It can lead to complications and adversely affect the outcomes of a surgical procedure. This can be due to various reasons. Let me elaborate.
When to stop smoking before surgery? The best time to stop smoking is now. The negative effects of smoking reduce after cessation of smoking. We usually advise a period of 4 to 6 weeks of abstinence before undertaking any surgery. Plastic surgery can involve extensive dissection of the tissues. This makes healing more dependent on adequate blood supply of the treated tissues. Because of the above reasons, smoking is a strong contrindication for surgery. Smoking is also one of the common reasons for postponement of the surgery in our practice. We usually choose to schedule surgery after a period of abstinence from smoking. For further reading about the effect of smoking during surgery, please visit: https://www.who.int/news/item/20-01-2020-smoking-greatly-increases-risk-of-complications-after-surgery Some of our patients come from another city or a faraway place. The reasons usually cited include, cost, and privacy. Even though most patients tend to have satisfying outcomes, getting surgery at a distant location has its challenges. The challenges usually relate to scheduling the surgery, arranging for a friend or relative to accompany during the surgery, and managing follow-up visits. Any postponement of the surgery can result in a lot of distress. One may need to schedule the surgery during the next vacation.
Being aware of the common reasons behind these issues can help one have a better experience. Let me list out some of the common reasons.
Even though consultation and clinical examination are the best means to assess a condition, examination of images can also give a fair idea of the treatment plan. For individuals who stay faraway, it is a good option to engage with the treatment provider with the help of emails and images. 2. Use of health supplements and smoking. Certain behaviors can result in an increased risk of surgical complications. These include smoking and intake of non-prescription health supplements. Smoking results in increased rates of infection, wound healing problems, and increased risk of bleeding. We insist on abstinence from smoking for one month before any procedure. Non-prescription health supplements maybe associated with an increased risk of bleeding. They should be avoided for a period of 2 to 4 weeks before surgery. Use of any such supplements must be brought to the notice of the health provider early on. 3. Presence of comorbidity (other illness) These include other diseases like diabetes and hypertension. These need not preclude a surgical procedure. However, they need to be medically optimized before undertaking any elective procedure. Some conditions may require a clearance by a medical speacialist. This helps avoid any untoward events during the procedure. Some individuals are prone to get skin conditions like folliculitis or acne eruptions. The presence of any skin infection close to the operated site may result in the postponement of the surgery. In case one tends to get such skin conditions it is recommended to undertake treatment by a doctor or a dermatologist before the surgery. These can be carried out with the help of a physician near the patient's place of stay. 4. Possibility of drug interactions. Some medicines being taken by the patient may interact with medicines used during anesthesia. For example, antihistamines used for allergies can influence the metabolism of lignocaine used during liposuction. We usually advise a drug holiday when there is a significant risk of drug interactions. In case an individual is taking any medicines for any related or unrelated condition, this should be brought to the notice of the surgeon. 5. Lack of a support system. Surgery is a stressful time even for the most well-prepared individual. Hence it is important to have someone like a reliable relative or a close friend during the recovery after surgery. We usually do not schedule patients for surgery when we are doubtful about the lack of adequate support during the immediate postoperative period. Postponement of the surgery is usually undertaken when we feel that some modification can result in better outcomes. These could mean the cessation of smoking or a drug holiday. It is also important for patients not to withhold any related or unrelated medical information because of any fear of postponement of the surgical procedure. To summarise, some of the key points for individuals who are planning to travel to another place for surgery include, interacting with the health provider early on, disclosing any related or unrelated health conditions, and avoiding any behavior that can increase the risk of complications. Structural fat grafting is a procedure that involves the transfer of fat cells from one part of the body to another. It is done because of various benefits such as improved volume of the treated areas, and tissue regeneration. Emulsified fat grafting is a different procedure during which the tissue is transferred without viable (living) adipocytes (fat cells). The emulsification helps get rid of any viable (living) fat cells.
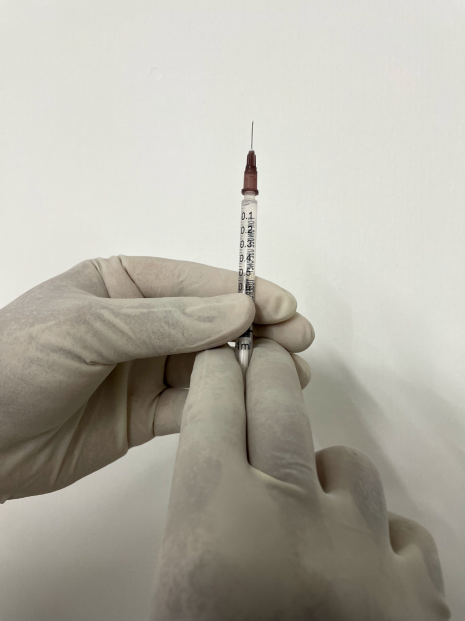
Why is emulsified fat grafting done? Unlike structural fat grafting, emulsified fat grafting does not result in increase in the volume of the treated areas. Instead, it leads to an improvement of the regenerative properties of the tissues. This results in improvement in the texture of skin, scars, or enhanced healing of wounds. How does emulsified fat grafting work? The fat containing tissues in have fat cells and supporting cells that help in growth and regeneration. The supporting cells are referred to as ADSC. During harvest, both adipocytes (fat cells) and the supporting cells are obtained together. The adipocytes or the fat cells are removed by mechanical disruption. The supporting cells are not affected by this process. These are injected into the body for their beneficial properties. Due to the absence of adipocytes, emulsified fat grafting does not lead to an increase in the volume of the grafted part. What are the various applications of emulsified fat grafting? Emulsified fat grafting helps the tissues in growth and repair. The various applications include
How is emulsified fat grafting performed? Emulsified fat grafting is usually carried out under local anesthesia as an outpatient procedure. The common areas for the harvest of fat are the abdomen or thighs. Small volumes are needed for this procedure. The harvested fat is then processed. The emulsified fat is then injected with the help of fine needles into the treated area. The treated areas are left open. The donor areas are treated with simple dressings that are removed after two days. What is the recovery from emulsified fat grafting? The donor area will have some firmness and induration that subsides over the next few weeks. The treated areas can show some swelling that subsides over days to weeks. The improvement in the texture of the skin takes a few weeks to become noticeable. In case of fat grafting into wounds, the following weeks may show accelerated healing. The changes in hair growth in case of injections for male pattern baldness may take a few weeks to become visible. What are the advantages of emulsified fat grafting? Emulsified fat grafting is beneficial across a variety of indications. It is also attractive since it is done as an outpatient procedure with a rapid recovery. The beneficial effects of the procedure are also long lasting. There is an increasing demand for cosmetic procedures with minimal downtime. The advantages are shorter recovery and the ability to return to normal life. One such procedure is non-surgical rhinoplasty.
What is a non-surgical rhinoplasty? It involves the injection of fillers into the nose to bring about a difference in appearance. It has more in common with a filler injection into the face than with a routine rhinoplasty. The 'rhinoplasty' in non-surgical rhinoplasty comes because the filler is being injected into the nose to alter its appearance. Non-surgical rhinoplasty is also referred to as liquid rhinoplasty. Why 'liquid'? Because the filler that is injected is a liquid. What are the advantages of doing a non-surgical rhinoplasty? The main advantage of such a procedure would be the minimal downtime. Since fillers are injected the time taken to complete the procedure would be very short and would not need any hospital admission. What can be achieved with non-surgical rhinoplasty? Compared to a surgical procedure, the benefits of a non-surgical procedure are limited. The benefits of a non-surgical rhinoplasty include,
What are the changes that can't be achieved with rhinoplasty? It is not possible to make a large nose smaller using injection non-surgical techniques. It is also not useful for the management of a bulbous tip. It is not possible to improve septal deviations with non-surgical rhinoplasty. Surgical rhinoplasty is the gold standard for the management of the deformities of the nose. How long does the effect of non-surgical rhinoplasty last? When compared to a surgical procedure, the effects of non-surgical rhinoplasty are temporary. In most cases, hyaluronic acid fillers are injected during this procedure. Hyaluronic acid breakdown with time. The effects may last approximately one to two years. In certain individuals, the effects tend to last for a shorter period. In case of an unfavourable result, it can be removed with the help of a hyaluronidase injection. What are the risks associated with non-surgical rhinoplasty? The risks associated with a non-surgical rhinoplasty are similar to those seen with filler injections into the face. These can include tissue death and involvement of the vessels of the eyes and brain. Skin necrosis results due to impaired blood supply of the skin. Embolization of the filler into the vessels of the eyes can lead to blindness. These adverse events have been reported with filler injections, they are uncommon. Who is a good candidate for non-surgical rhinoplasty? It would include patients who want a change in the appearance of the nose without any downtime or need for aftercare associated with a conventional rhinoplasty. Patients should have realistic expectations and understand that not all deformities can be improved with a non-surgical rhinoplasty. The effects are temporary and need repeat injections for maintenance of the results. For more information about rhinoplasty please visit: www.amicusclinic.in/rhinoplasty |
AuthorI like to keep it simple. CategoriesArchives
June 2024
Categories |
- Home
-
Cosmetic
- Fat grafting
- Swellings and moles
- Scar revision
- Leukoderma (Melanocyte transfer)
- Hair transplant
- Facial rejuvenation procedures
- Nose job (Rhinoplasty)
- Cleft lip nose correction
- Ear (Otoplasty)
- Lip reduction
- Breast augmentation
- Breast reduction
- Tuberous breasts
- Axillary breasts
- Gynecomastia
- Liposuction
- Brachioplasty (Arm contouring)
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy tuck)
- Female genital rejuvenation
-
Reconstructive
- Contact
- Blog
- Home
-
Cosmetic
- Fat grafting
- Swellings and moles
- Scar revision
- Leukoderma (Melanocyte transfer)
- Hair transplant
- Facial rejuvenation procedures
- Nose job (Rhinoplasty)
- Cleft lip nose correction
- Ear (Otoplasty)
- Lip reduction
- Breast augmentation
- Breast reduction
- Tuberous breasts
- Axillary breasts
- Gynecomastia
- Liposuction
- Brachioplasty (Arm contouring)
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy tuck)
- Female genital rejuvenation
-
Reconstructive
- Contact
- Blog
You can leave us a comment using the contact form below.
We shall get back to you at the earliest.
We shall get back to you at the earliest.
Links
- Face procedures | Rhinoplasty, Otoplasty, Lip reduction, Fat grafting
- Body procedures | Gynecomastia , Breast reduction, Abdominoplasty, Brachioplasty, Liposuction
- Skin procedures | Scar revision, Moles, Leukoderma surgery
Let's be friends !
Follow us at Facebook and Twitter.
Follow us at Facebook and Twitter.
© 2024 Amicus Clinic (Plastic Surgery Centre, Trivandrum). All rights reserved.


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed



