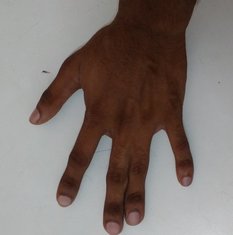
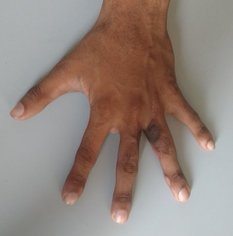
Syndactyly
Syndactyly refers to the abnormal fusion between digits of the hand or foot. It is the most common congenital abnormality of the hand. Syndactyly results in impaired function of the hand.
What causes syndactyly?
It is as a result of abnormal differentiation between the digits during development. It tends to run in families. Syndactyly also occurs as a part of various syndromes.
What are the different types of syndactyly?
Depending on the presentation, it can be classified into:
Syndactyly is complete when the fusion extends up to the fingertips. Incomplete syndactyly stops short of the fingertips.
What is the treatment for syndactyly?
Syndactyly is surgically treated to improve the functionality of the affected hands.
Surgical treatment is carried out after 6 months of age. The fused digits are separated with the help of local flaps and skin grafts. Staged correction is done in cases when both sides of a digit are involved. Early correction facilitates the normal growth of the digits.
Central syndactyly between the middle and ring fingers can be corrected at about 2 years of age since it does not cause a significant deviation in the normal growth of the central digits.
In case both hands are involved, simultaneous correction is undertaken tolerated below 18 months of age. Unilateral corrections are undertaken in older children.
What causes syndactyly?
It is as a result of abnormal differentiation between the digits during development. It tends to run in families. Syndactyly also occurs as a part of various syndromes.
What are the different types of syndactyly?
Depending on the presentation, it can be classified into:
- Simple syndactyly
- Complex syndactyly
- Complicated syndactyly
Syndactyly is complete when the fusion extends up to the fingertips. Incomplete syndactyly stops short of the fingertips.
What is the treatment for syndactyly?
Syndactyly is surgically treated to improve the functionality of the affected hands.
Surgical treatment is carried out after 6 months of age. The fused digits are separated with the help of local flaps and skin grafts. Staged correction is done in cases when both sides of a digit are involved. Early correction facilitates the normal growth of the digits.
Central syndactyly between the middle and ring fingers can be corrected at about 2 years of age since it does not cause a significant deviation in the normal growth of the central digits.
In case both hands are involved, simultaneous correction is undertaken tolerated below 18 months of age. Unilateral corrections are undertaken in older children.