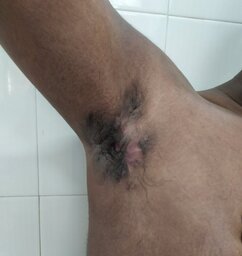
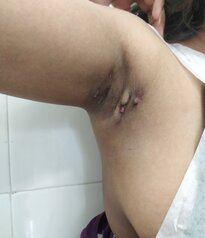
HIDRADENITIS SUPPURATIVA
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a skin condition in which individuals tend to get recurrent painful swellings, which rupture and lead to the formation of sinuses. Sinuses are openings in the skin that communicate with deeper tissues. Certain areas of the body are prone to get affected by this condition. These include the skin of the axilla (armpit), under the breasts, the groin (the region where the abdomen meets the thigh), and skin between the buttocks. Some individuals tend to get contractures in the affected areas. Contractures refer to a type of scar that results in a limitation in the range of motion. It can also result in the formation of keloids. The disease is associated with progressive scarring of the affected areas. This disease is usually chronic. It means the disease tends to recur. A clinical examination helps in reaching a diagnosis.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is seen in men and women. It is seen in otherwise healthy individuals. Women tend to be more commonly affected by this condition. It is uncommon before adolescence. Pregnancy can result in remission in some individuals. This disease tends to be seen in individuals with acne. Obesity and smoking are also seen more commonly in such individuals. The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is not known. It is associated with the inflammation of the structures surrounding the hair follicles. Some individuals tend to have joint-related symptoms such as pain and swelling.
Treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa:
Medical management is indicated in the acute or early presentation. The early stages include the appearance of erythema (redness) and painful swellings. Conservative treatment in the early stages includes local hygiene and warm compresses. The use of loose-fitting clothes and laser hair removal is advised. In case an individual is overweight they are encouraged to lose weight. Smoking should be avoided. Different classes of medicines are used for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. These include antibiotics, analgesics, retinoids, steroids, etc. These should be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Surgery is indicated in chronic and recurrent cases. Surgery can be limited or more aggressive with the removal of the affected skin and coverage with a skin graft or flap. Limited forms of surgical interventions include drainage of abscesses, curettage, and deroofing of cavities and allowing it to heal by secondary intention (wound closes spontaneously by healing from the edges). Aggressive surgical treatment is associated with the least incidence of recurrence.
It is a chronic condition that can result in disabling symptoms. It can lead to anxiety and depression. The treatment depends on the clinical presentation. With aggressive surgery, it is possible to have reduced recurrence and improvement in the quality of life.
Hidradenitis suppurativa is seen in men and women. It is seen in otherwise healthy individuals. Women tend to be more commonly affected by this condition. It is uncommon before adolescence. Pregnancy can result in remission in some individuals. This disease tends to be seen in individuals with acne. Obesity and smoking are also seen more commonly in such individuals. The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is not known. It is associated with the inflammation of the structures surrounding the hair follicles. Some individuals tend to have joint-related symptoms such as pain and swelling.
Treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa:
Medical management is indicated in the acute or early presentation. The early stages include the appearance of erythema (redness) and painful swellings. Conservative treatment in the early stages includes local hygiene and warm compresses. The use of loose-fitting clothes and laser hair removal is advised. In case an individual is overweight they are encouraged to lose weight. Smoking should be avoided. Different classes of medicines are used for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa. These include antibiotics, analgesics, retinoids, steroids, etc. These should be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist.
Surgery is indicated in chronic and recurrent cases. Surgery can be limited or more aggressive with the removal of the affected skin and coverage with a skin graft or flap. Limited forms of surgical interventions include drainage of abscesses, curettage, and deroofing of cavities and allowing it to heal by secondary intention (wound closes spontaneously by healing from the edges). Aggressive surgical treatment is associated with the least incidence of recurrence.
It is a chronic condition that can result in disabling symptoms. It can lead to anxiety and depression. The treatment depends on the clinical presentation. With aggressive surgery, it is possible to have reduced recurrence and improvement in the quality of life.