|
Gynecomastia is enlargement of male breasts. It can be a cause of significant anxiety and embarrassment in those affected by this condition. Surgical correction results in a long-term improvement in appearance. The different options available for a surgical cure include: 1. Liposuction: This involves removal of fat cells with thin tubes attached to a suction device. The suction can be produced with a machine or a syringe. The fat cells are permanently removed from the treated site resulting in a flattened contour. Liposuction is especially useful when gynaecomastia is mostly due to fatty tissue. 2. Gland excision: The glandular tissue also contributes to a varying extent in gynecomastia. This is more amenable to direct excision. The placement of incision can be at, a) Intraareolar: The areola is the pigmented skin surrounding the nipple. The incision and the resulting scar lies within the areola. This usually results in a scar which is not easily made out. b) Periareolar: Here the incision lies at the junction of pigmented and non-pigmented skin. It heals with a light-colored scar. 3. Skin excision: In certain cases of long standing gynecomastia there may be an excess of skin with a reduced ability to recoil. In such situations, a disc of skin is removed for treatment of the excess skin. The removal of skin can also be done at a later stage to allow for the natural recoil of the skin. All these modalities can be combined in one procedure depending on the severity of gynecomastia. Postoperatively dressings are removed during the next day. Drainage tubes are sometimes placed to evacuate fluids from the operated site. They are usually removed during the first few days. Sutures are removed after seven days. Patients can return to work after one week. Workouts and heavy exertion can be resumed after six weeks.
What are keloids?
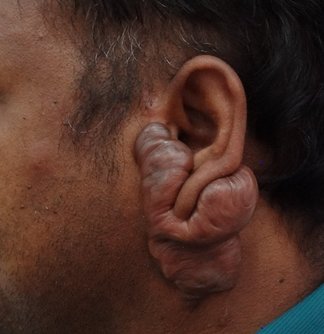
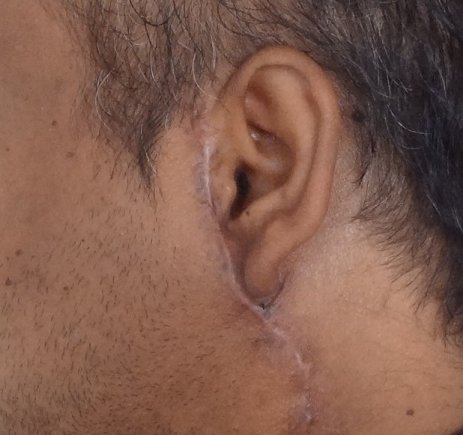
They are prominent scars which grow beyond the boundaries of the original wound. They can follow trauma, infection, burns or any other type of injury. What are the symptoms of keloids? They are commonly associated with the following, 1. Pain 2. Itching 3. Cosmetic deformity What causes keloids? The exact reasons are not known. It has been found to occur in all types of skin. It is less common among elderly. A tendency for keloid scarring is known to run in families. What are the most common sites of keloids? These include, 1. Ear lobes 2. Chest 3. Back 4. Jawline What are the treatment options for keloids? Large keloids are more difficult to treat when compared to smaller ones. The treatment options include, 1. Intralesional injection of steroids: These have to be repeated at regular intervals for improvement in appearance and texture. 2. Silicone sheet application: Silicone sheets have to be applied for prolonged periods. 3. Pressure garment: These can be applied with the help of a custom made garment. 4. Radiotherapy 5. Intralesional injection of 5 fluorouracil 6. Surgery The combination of more than one modality of treatment is advised in case of large keloids. Surgery is useful for debulking ( reducing the size ) a keloid. It has to be followed up with another modality like intralesional injections or use of pressure garment. What is the role of prevention? The possibility of keloid formation following surgery should be borne in mind in persons with a tendency for keloid formation. Measures such as the use of silicone sheet and pressure garment are advised early in the post operative period. To learn more about other types of scars, click here. |
AuthorI like to keep it simple. CategoriesArchives
June 2024
Categories |
- Home
-
Cosmetic
- Fat grafting
- Swellings and moles
- Scar revision
- Leukoderma (Melanocyte transfer)
- Hair transplant
- Facial rejuvenation procedures
- Nose job (Rhinoplasty)
- Cleft lip nose correction
- Ear (Otoplasty)
- Lip reduction
- Breast augmentation
- Breast reduction
- Tuberous breasts
- Axillary breasts
- Gynecomastia
- Liposuction
- Brachioplasty (Arm contouring)
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy tuck)
- Female genital rejuvenation
-
Reconstructive
- Contact
- Blog
- Home
-
Cosmetic
- Fat grafting
- Swellings and moles
- Scar revision
- Leukoderma (Melanocyte transfer)
- Hair transplant
- Facial rejuvenation procedures
- Nose job (Rhinoplasty)
- Cleft lip nose correction
- Ear (Otoplasty)
- Lip reduction
- Breast augmentation
- Breast reduction
- Tuberous breasts
- Axillary breasts
- Gynecomastia
- Liposuction
- Brachioplasty (Arm contouring)
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy tuck)
- Female genital rejuvenation
-
Reconstructive
- Contact
- Blog
You can leave us a comment using the contact form below.
We shall get back to you at the earliest.
We shall get back to you at the earliest.
Links
- Face procedures | Rhinoplasty, Otoplasty, Lip reduction, Fat grafting
- Body procedures | Gynecomastia , Breast reduction, Abdominoplasty, Brachioplasty, Liposuction
- Skin procedures | Scar revision, Moles, Leukoderma surgery
Let's be friends !
Follow us at Facebook and Twitter.
Follow us at Facebook and Twitter.
© 2024 Amicus Clinic (Plastic Surgery Centre, Trivandrum). All rights reserved.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed



