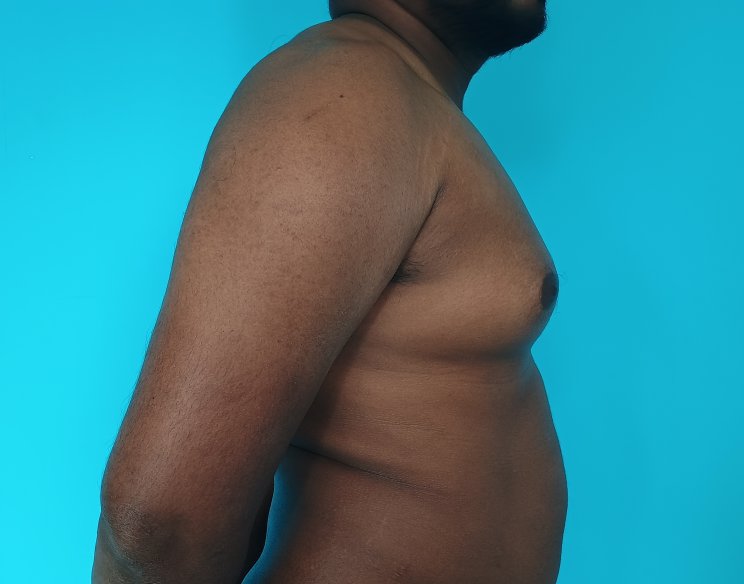
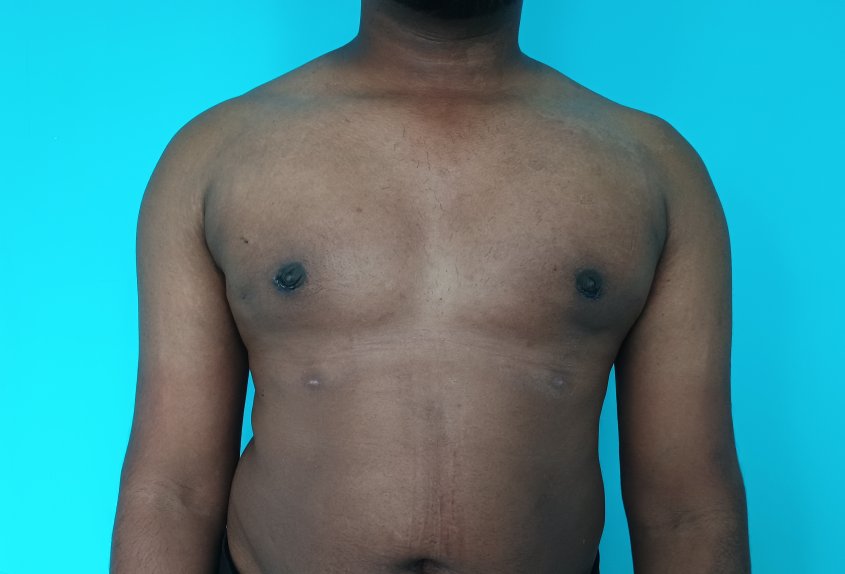
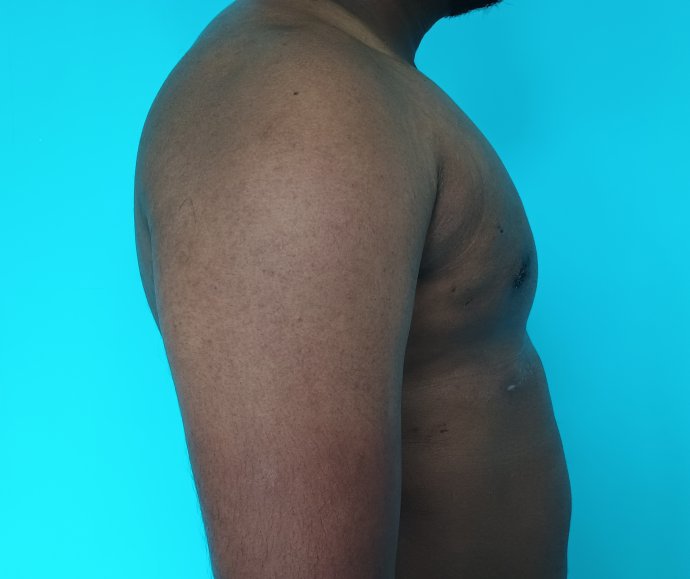
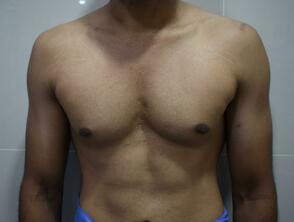
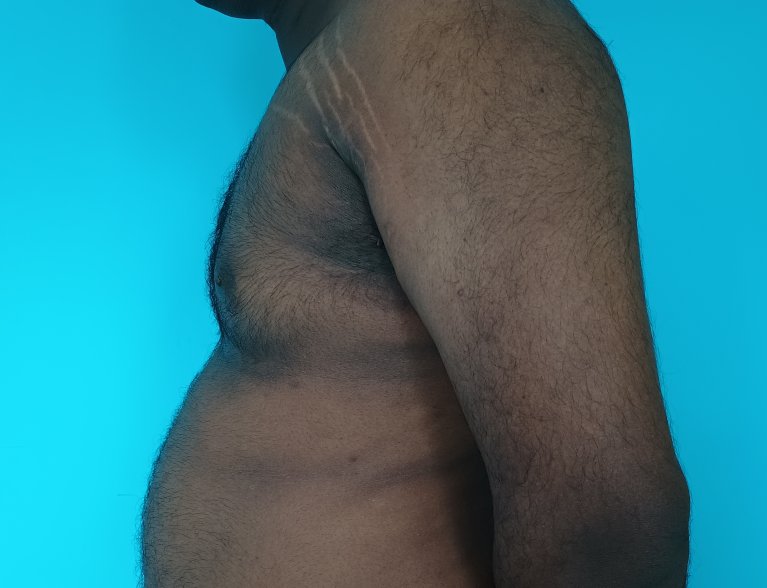
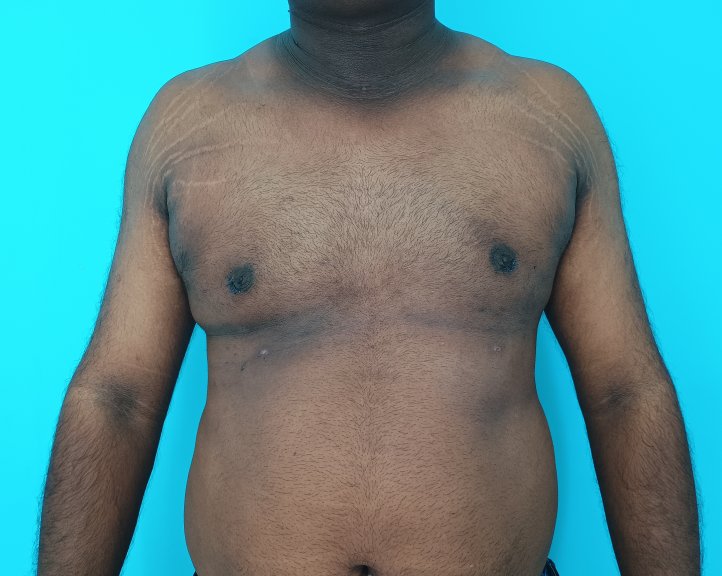
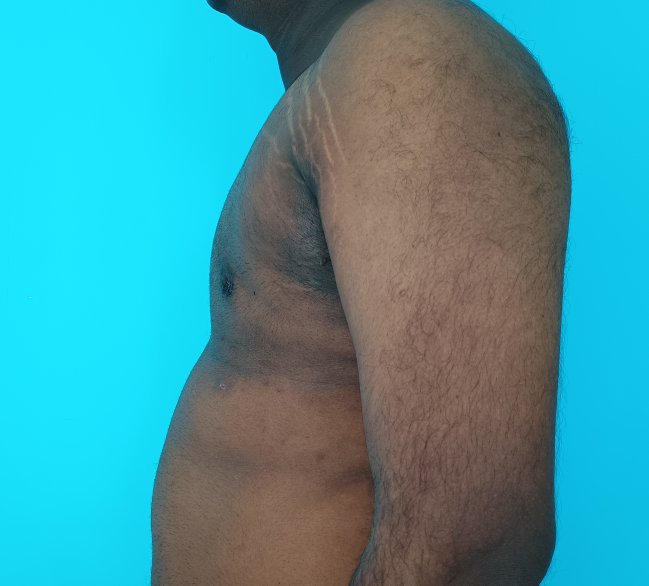
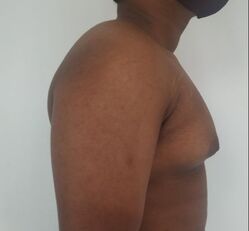
GYNECOMASTIA (ENLARGED MALE BREASTS)
Gynecomastia is an enlargement of the male breast tissue. Because of this, it causes a feminine appearance to the male chest. It is a common condition and is often associated with a sense of shame and embarrassment in the affected individual.
Do I have gynecomastia?
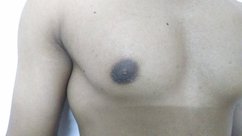
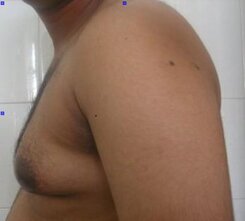
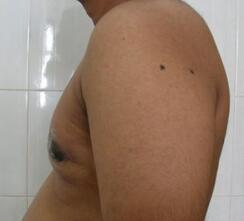
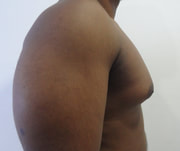
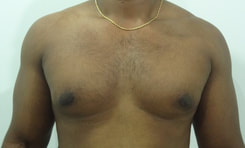
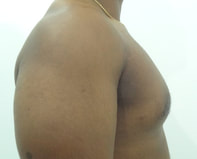
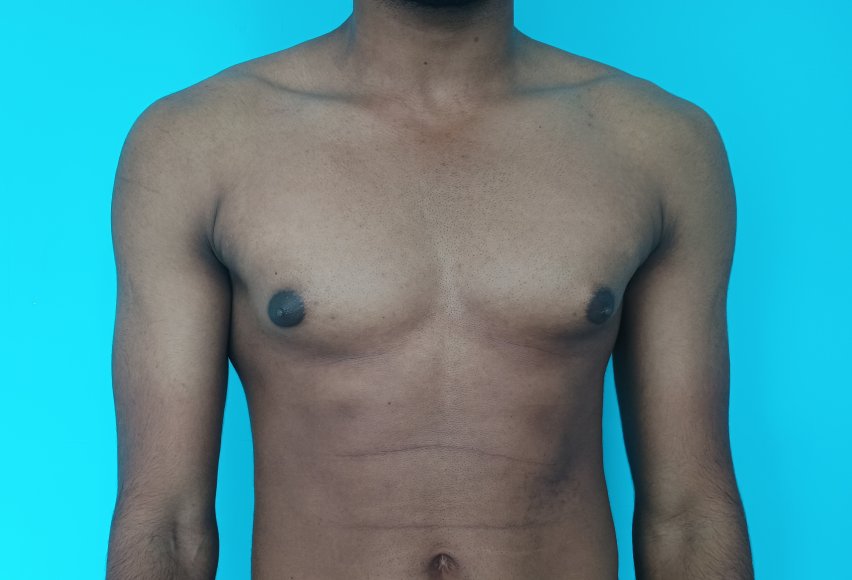
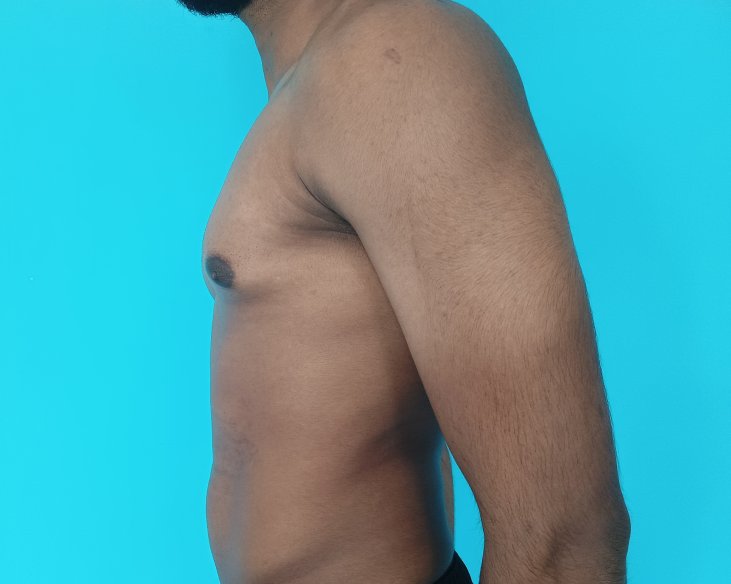
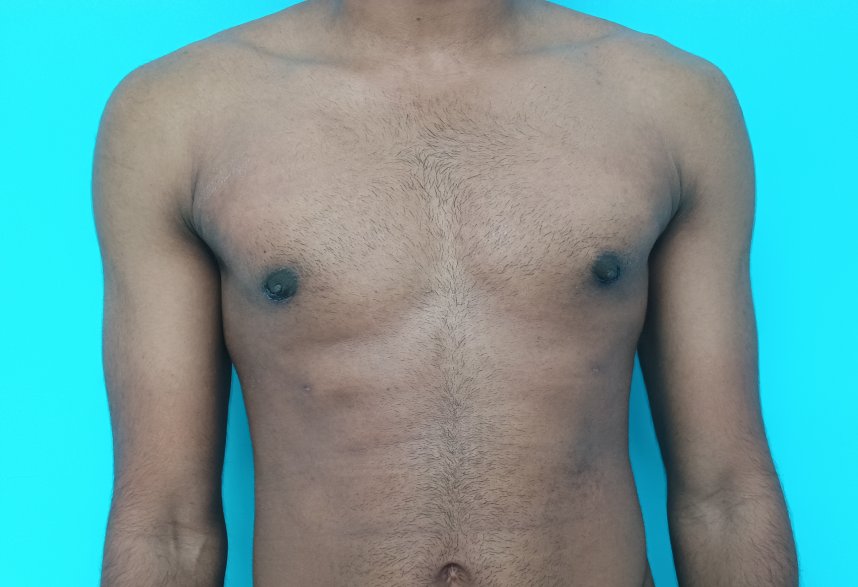
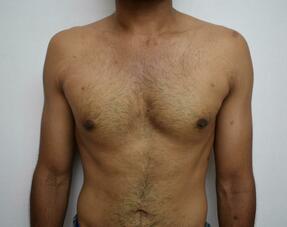
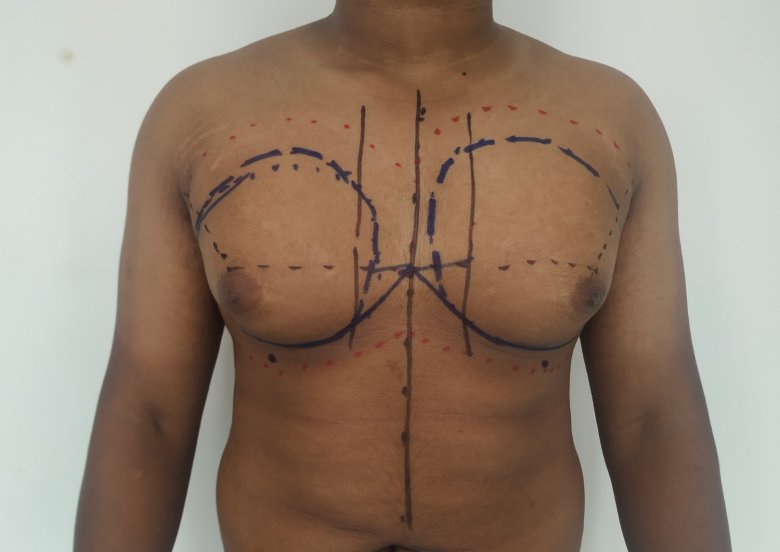
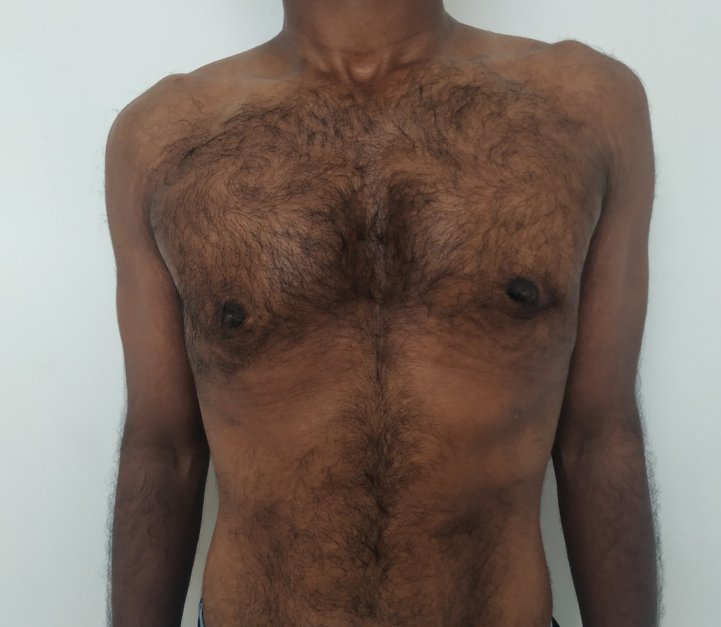
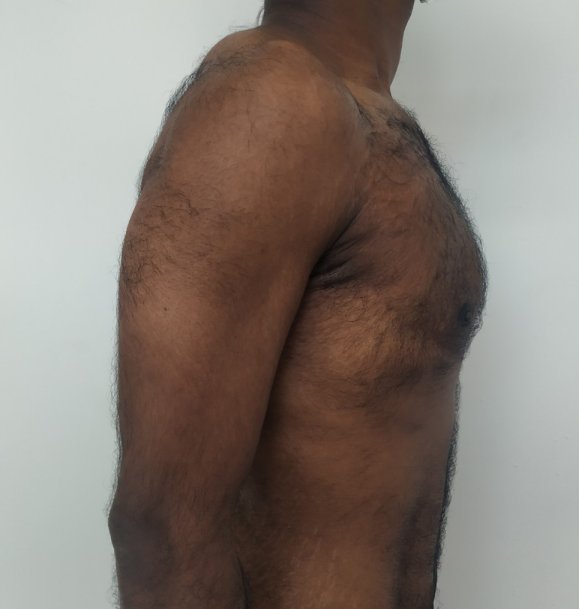
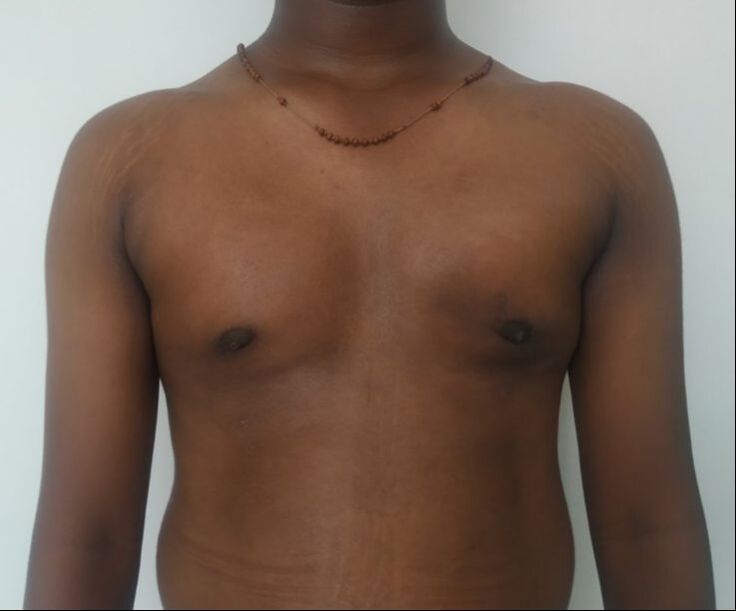
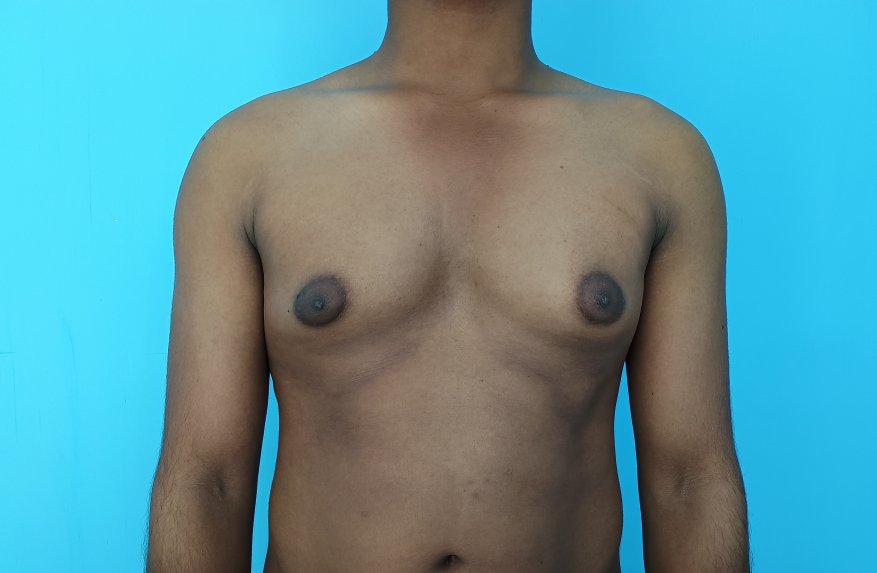
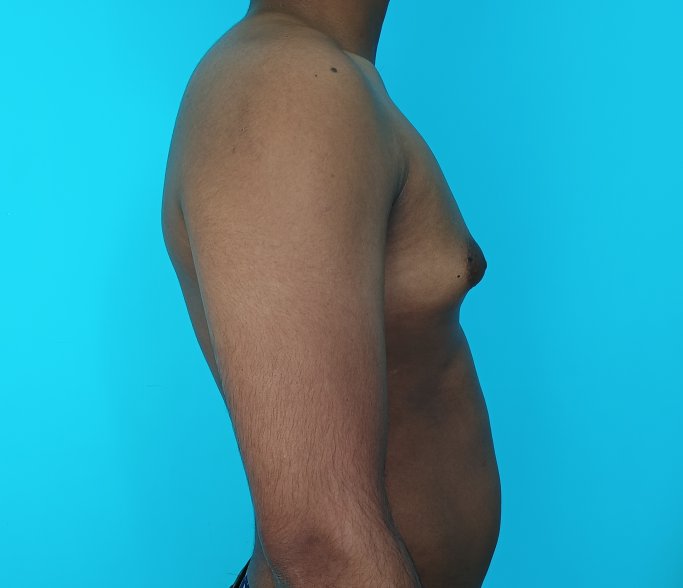
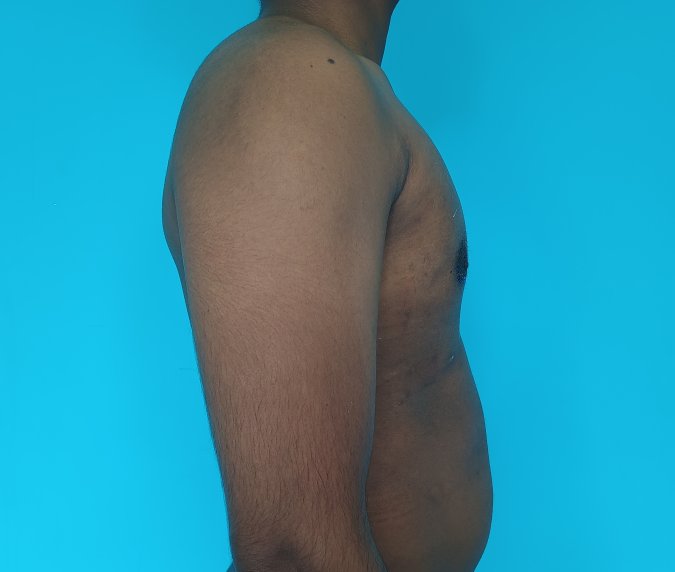
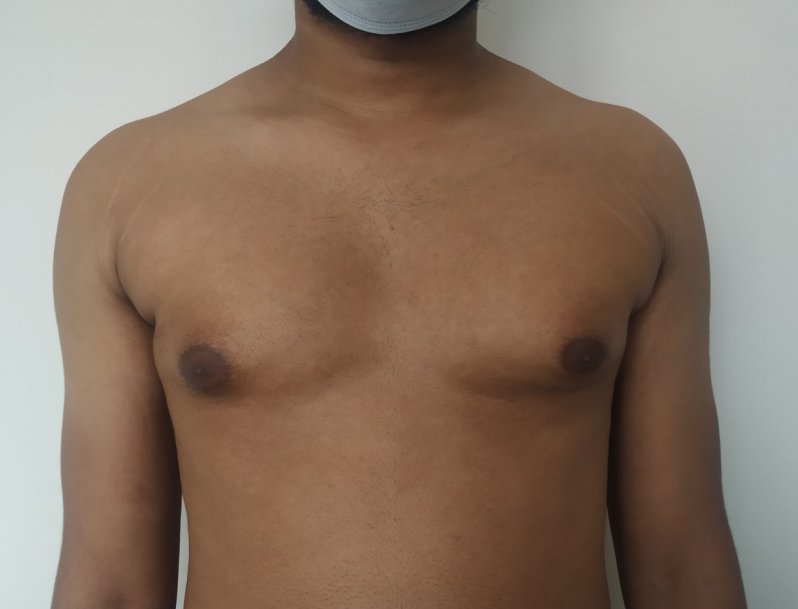
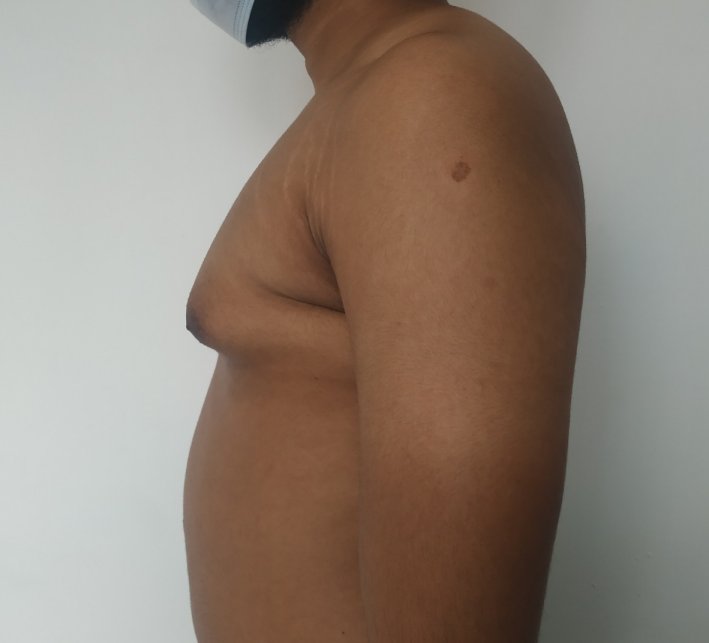
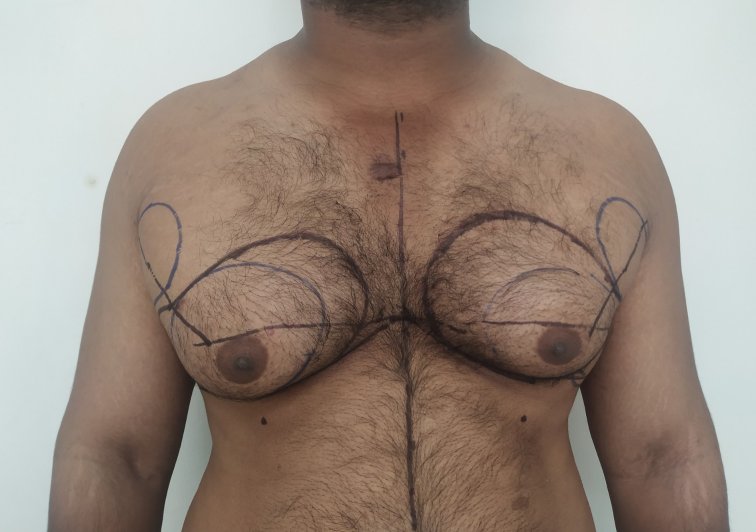
Gynecomastia is a deformity. A breast that looks more prominent in the lower part is usually due to gynecomastia. In case an individual is affected by the appearance of his chest, there is a good likelihood that he has gynecomastia. A clinical examination is adequate to ascertain the diagnosis. Gynecomastia can have varied presentations. It can affect one, or both sides of the chest. One of the sides may be affected more than the other. Some individuals may present with only a prominence of the skin around the nipple. In some individuals with massive weight loss, there can be significant sagging of the breast tissues.
What causes gynecomastia?
In the majority, gynecomastia occurs without an identifiable cause. These are primary or idiopathic gynecomastia. In some, it can be secondary to some other cause. For example, certain drugs, and systemic diseases of liver, kidney, or chromosomal abnormalities can lead to gynecomastia. We usually screen individuals presenting with gynecomastia with an assessment of levels of a few hormones. Normal levels of these are seen in primary gynecomastia. Any significant abnormality in the levels of these hormones is further evaluated with the help of an endocrinologist (specialist in the treatment of diseases of hormones).
What is the treatment of gynecomastia?
Definitive treatment of gynecomastia is with surgery. There is a limited role of medications in the management of this condition. A course of Tamoxifen is sometimes advised in individuals with painful gynecomastia.
Can exercise lead to a resolution of gynecomastia?
No. However, exercise can have two positive outcomes. One is weight loss, and the second is an improved definition (contour) of the chest. Weight training can lead to a hypertrophy of the chest muscles. But it can't lead to a reduction in the glandular tissue of the breasts. An increase in the bulk of chest muscles (pectorals) causes an increase in the projection of the chest.
When is a good time to do surgery on an individual with gynecomastia?
Most of our patients presenting for correction are those with persistence (continuation) of puberty onset gynecomastia. We usually advise our patients to wait until 18 years of age before undertaking a surgical correction. This is because many of the instances of pubertal onset gynecomastia resolve before 18. We uncommonly operate in individuals before 18. This is done in cases with extreme enlargement, and associated with significant emotional distress. Individuals undergoing surgery before 18 also have an increased risk of recurrence. A patient with realistic expectations of the outcome and in good health are good candidates for surgical correction.
How does a patient undergo surgical correction?
When a patient first presents for a consultation, he is clinically evaluated. Any risk factors for secondary gynecomastia. We evaluate the presence of skin excess. Patients are screened for any risk factors that can influence the outcome of the surgical procedure. We make a surgical plan based on the clinical findings. Patients are counseled regarding the treatment plan, possible outcomes, recovery, and potential complications. We also advise a few laboratory tests. These include assessment of levels of hormones and other blood parameters. In case, a patient has realistic expectations and does not have any modifiable risk factors we go ahead with the surgery at a later date.
What are the common modifiable risk factors of gynecomastia surgery?
The two most common modifiable risk factors that we come across in our practice are,
How is the surgery performed?
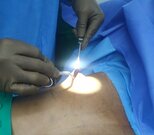
Most of our patients with gynecomastia get operated under local anesthesia. This is combined with intravenous sedation. Less commonly, we perform the surgery under general anesthesia. This is usually reserved for anxious individuals. General anesthesia is also administered for those who need skin excision. After a staged infiltration of a tumescent (numbing) solution, we first carry out liposuction of the chest. Liposuction helps reduce the fatty tissue through small incisions. The incisions are less than half a centimeter long and are placed about 10 cm below the nipple. We do not place the entry ports for liposuction in the axilla. We use syringe liposuction in our practice. It offers the benefits of being quiet and helps us to symmetrize the residual fat left behind.
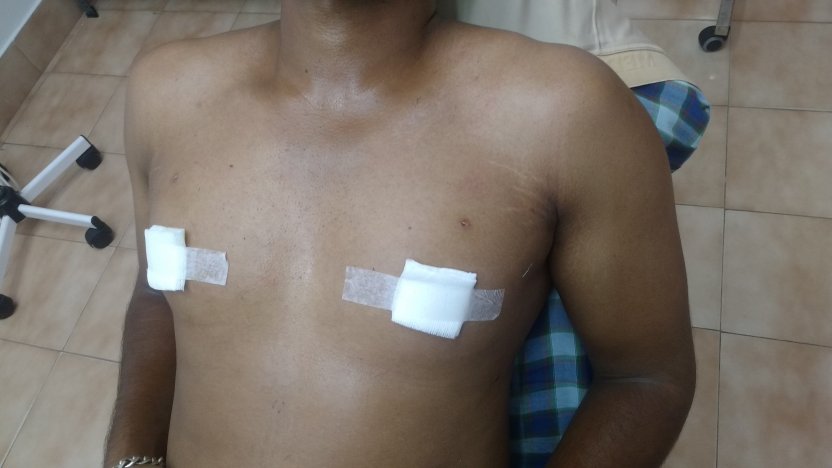
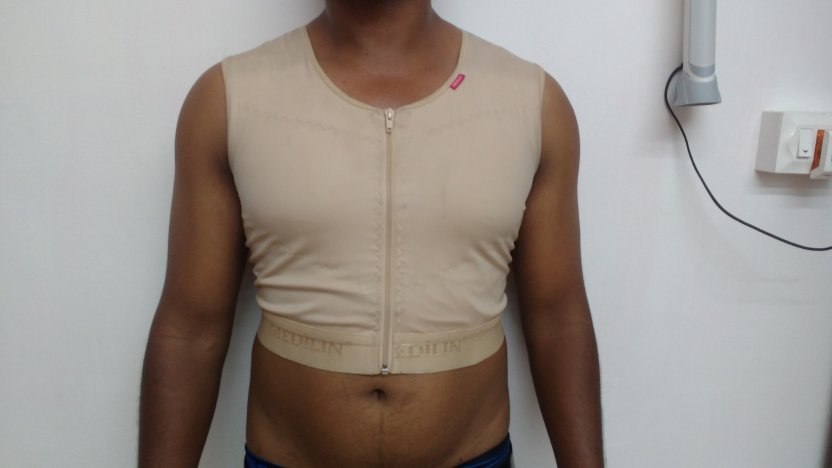
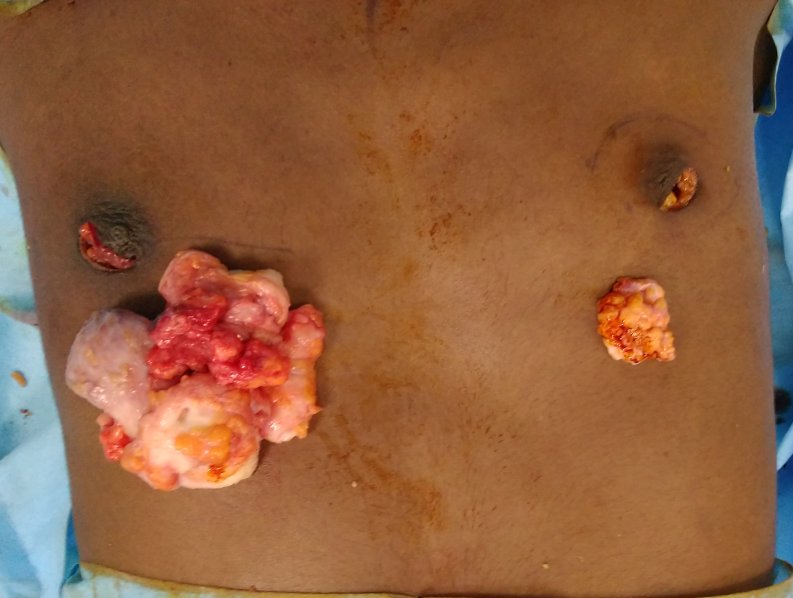
Liposuction is done on both the anterior (front) and the lateral (side) chest. After liposuction, a small incision is made in the areola(pigmented skin around the nipple), and the gland is removed directly under vision. The areolar incision is closed with the help of small sutures (stitches). The drains (small tubes that evacuate fluids) come out through the skin incisions used for liposuction. The drains are usually removed during the next day. Once the drains are removed patients are put on a pressure garment. A pressure garment is a vest that helps to minimize the swelling after surgery. It also helps reduce the incidence of contour abnormalities. The vest is worn for four weeks after surgery.
What is the postoperative care required after surgery?
When done under local anesthesia, patients can move about soon after surgery. We advise our patients to take a lot of rest during the initial 3 days. Patients can move about. Rest during the initial days helps minimize the chances of any reactionary hemorrhage (bleeding that happens during the initial 2 to 3 days) at the operated site. Patients can take a shower on the second postoperative day. The wounds are covered with a small dressing, and the pressure garment is worn over it. The garment is worn continuously for the first 2 weeks and at night for the next 2 weeks. Patients can return to light work, after 2 weeks. We usually remove the areolar sutures at 2 weeks. Individuals can resume heavy exercise one month after the surgery. There are no restrictions for any activities after a month.
What are the changes usually associated with normal healing?
Any type of surgery is associated with swelling at the operated sites. This is a normal occurrence. Some of the patients tend to have more bruising than others. This usually subsides without any intervention. Application of cold helps in earlier resolution of the bruising. The swelling at the operated site reduces with time. It usually takes approximately 3 months for the swelling to settle on the sides of the chest. The swelling may not resolve uniformly over the operated site. This may lead to areas of intervening firmness separated by relatively softer areas temporarily. However, it settles over the next few weeks without any intervention.
What are the complications associated with gynecomastia correction?
Gynecomastia correction is a safe surgery. Complications are not that common. Some of the complications that can be seen include,
What are the other operative plans used during gynecomastia correction?
The previously mentioned operative approach is sometimes modified based on the clinical findings. Two common variations include,
What are the differences between local and general anesthesia when used for correction of gynecomastia?
Both local and general anesthesia have relative merits and demerits. We prefer local anesthesia in our practice and reserve general anesthesia for individuals who are anxious or need skin excision. The advantages of local anesthesia for gynecomastia correction include the following,
Is it possible to undergo secondary (repeat) surgery after a previous gynecomastia correction?
Such corrections are called secondary corrections. These are usually carried out one year after the primary surgery. The reasons for secondary surgery include contour abnormalities, the presence of residual glands, or prominent scars. Patients who present for secondary corrections should have realistic expectations about the procedure. The operative plan for secondary surgery is similar to the primary surgery. We sometimes carry out fat grafting to improve contour abnormalities. The fat harvested during liposuction is injected into deficient areas. We tend to see improved outcomes with a healthy lifestyle and near-ideal body weight.
Why do we treat gynecomastia?
In case an individual is experiencing a sense of shame and embarrassment because of gynecomastia, adequate treatment of this condition leads to an improvement in body image. Patients report improved confidence and self-esteem after a gynecomastia correction.
Related topics.
Do I have gynecomastia?
Gynecomastia is a deformity. A breast that looks more prominent in the lower part is usually due to gynecomastia. In case an individual is affected by the appearance of his chest, there is a good likelihood that he has gynecomastia. A clinical examination is adequate to ascertain the diagnosis. Gynecomastia can have varied presentations. It can affect one, or both sides of the chest. One of the sides may be affected more than the other. Some individuals may present with only a prominence of the skin around the nipple. In some individuals with massive weight loss, there can be significant sagging of the breast tissues.
What causes gynecomastia?
In the majority, gynecomastia occurs without an identifiable cause. These are primary or idiopathic gynecomastia. In some, it can be secondary to some other cause. For example, certain drugs, and systemic diseases of liver, kidney, or chromosomal abnormalities can lead to gynecomastia. We usually screen individuals presenting with gynecomastia with an assessment of levels of a few hormones. Normal levels of these are seen in primary gynecomastia. Any significant abnormality in the levels of these hormones is further evaluated with the help of an endocrinologist (specialist in the treatment of diseases of hormones).
What is the treatment of gynecomastia?
Definitive treatment of gynecomastia is with surgery. There is a limited role of medications in the management of this condition. A course of Tamoxifen is sometimes advised in individuals with painful gynecomastia.
Can exercise lead to a resolution of gynecomastia?
No. However, exercise can have two positive outcomes. One is weight loss, and the second is an improved definition (contour) of the chest. Weight training can lead to a hypertrophy of the chest muscles. But it can't lead to a reduction in the glandular tissue of the breasts. An increase in the bulk of chest muscles (pectorals) causes an increase in the projection of the chest.
When is a good time to do surgery on an individual with gynecomastia?
Most of our patients presenting for correction are those with persistence (continuation) of puberty onset gynecomastia. We usually advise our patients to wait until 18 years of age before undertaking a surgical correction. This is because many of the instances of pubertal onset gynecomastia resolve before 18. We uncommonly operate in individuals before 18. This is done in cases with extreme enlargement, and associated with significant emotional distress. Individuals undergoing surgery before 18 also have an increased risk of recurrence. A patient with realistic expectations of the outcome and in good health are good candidates for surgical correction.
How does a patient undergo surgical correction?
When a patient first presents for a consultation, he is clinically evaluated. Any risk factors for secondary gynecomastia. We evaluate the presence of skin excess. Patients are screened for any risk factors that can influence the outcome of the surgical procedure. We make a surgical plan based on the clinical findings. Patients are counseled regarding the treatment plan, possible outcomes, recovery, and potential complications. We also advise a few laboratory tests. These include assessment of levels of hormones and other blood parameters. In case, a patient has realistic expectations and does not have any modifiable risk factors we go ahead with the surgery at a later date.
What are the common modifiable risk factors of gynecomastia surgery?
The two most common modifiable risk factors that we come across in our practice are,
- Smoking. Smoking is associated with an increased risk of infection, hematomas, increased bleeding during surgery, and wound healing problems. It is strongly recommended to stop smoking at least one month before the surgery and during the postoperative period. Smoking is a reason for the postponement of the surgery in our practice.
- Increased body weight. Better outcomes are seen in individuals close to their ideal body weight. Obesity is associated with more extensive surgery and a greater risk of wound-related complications. In case an overweight individual is planning to undergo gynecomastia surgery after a few months, it is advisable to reduce their weight before surgery.
- Use of vitamin and herbal supplements. Some vitamins and herbal supplements are associated with an increased risk of bleeding. We usually ask our patients to stop supplements for two weeks before the planned date of surgery.
- Uncontrolled co-morbid illness. Any co-morbid illness should be treated adequately for better outcomes. These include liver dysfunction and diabetes. A specialist opinion is usually sought for help in the management of such conditions.
How is the surgery performed?
Most of our patients with gynecomastia get operated under local anesthesia. This is combined with intravenous sedation. Less commonly, we perform the surgery under general anesthesia. This is usually reserved for anxious individuals. General anesthesia is also administered for those who need skin excision. After a staged infiltration of a tumescent (numbing) solution, we first carry out liposuction of the chest. Liposuction helps reduce the fatty tissue through small incisions. The incisions are less than half a centimeter long and are placed about 10 cm below the nipple. We do not place the entry ports for liposuction in the axilla. We use syringe liposuction in our practice. It offers the benefits of being quiet and helps us to symmetrize the residual fat left behind.
Liposuction is done on both the anterior (front) and the lateral (side) chest. After liposuction, a small incision is made in the areola(pigmented skin around the nipple), and the gland is removed directly under vision. The areolar incision is closed with the help of small sutures (stitches). The drains (small tubes that evacuate fluids) come out through the skin incisions used for liposuction. The drains are usually removed during the next day. Once the drains are removed patients are put on a pressure garment. A pressure garment is a vest that helps to minimize the swelling after surgery. It also helps reduce the incidence of contour abnormalities. The vest is worn for four weeks after surgery.
What is the postoperative care required after surgery?
When done under local anesthesia, patients can move about soon after surgery. We advise our patients to take a lot of rest during the initial 3 days. Patients can move about. Rest during the initial days helps minimize the chances of any reactionary hemorrhage (bleeding that happens during the initial 2 to 3 days) at the operated site. Patients can take a shower on the second postoperative day. The wounds are covered with a small dressing, and the pressure garment is worn over it. The garment is worn continuously for the first 2 weeks and at night for the next 2 weeks. Patients can return to light work, after 2 weeks. We usually remove the areolar sutures at 2 weeks. Individuals can resume heavy exercise one month after the surgery. There are no restrictions for any activities after a month.
What are the changes usually associated with normal healing?
Any type of surgery is associated with swelling at the operated sites. This is a normal occurrence. Some of the patients tend to have more bruising than others. This usually subsides without any intervention. Application of cold helps in earlier resolution of the bruising. The swelling at the operated site reduces with time. It usually takes approximately 3 months for the swelling to settle on the sides of the chest. The swelling may not resolve uniformly over the operated site. This may lead to areas of intervening firmness separated by relatively softer areas temporarily. However, it settles over the next few weeks without any intervention.
What are the complications associated with gynecomastia correction?
Gynecomastia correction is a safe surgery. Complications are not that common. Some of the complications that can be seen include,
- Infection. It is uncommon. To reduce the incidence of infection we perform the surgery under antibiotics. In case of the presence of any locus of infection like folliculitis (boil) detected near the site of surgery, we postpone the surgery until the skin infection has resolved.
- Collections. This refers to the accumulation of fluids at the operated site. This is less common when we perform the surgery under local anesthesia. Reducing physical activity during the initial days and placement of a drain help reduce the incidence of collections. In case an individual develops a collection, it is managed depending on the severity. Small collections are treated without any intervention. They settle by themselves. In the presence of collections of about 10 ml or more, we perform a needle and syringe evacuation after 2 weeks. In case an individual has a large hematoma, we evacuate by taking the individual back to the operation theatre. Such events are uncommon.
- Prominent scars. The scars associated with gynecomastia surgery are usually well tolerated. They may be associated with pigment (color) abnormalities and small unevenness during the early postoperative period. These settle well in a few months. Some individuals tend to get prominent scars. They would require additional care in the postoperative period with the help of silicone sheets. We do not consider hypertrophic scarring tendency as a contraindication for gynecomastia surgery.
- Contour abnormalities. These are usually uncommon in individuals with adequate skin recoil. In case there is a persistence of contour abnormalities after a year, it may require additional surgery for correction.
- Recurrence of gynecomastia. This is usually seen in individuals who get operated on before 18 years. Otherwise, it is not common.
What are the other operative plans used during gynecomastia correction?
The previously mentioned operative approach is sometimes modified based on the clinical findings. Two common variations include,
- Gland excision without liposuction. This is sometimes done in thin individuals with very little fatty tissue in the breasts. These individuals usually present as puffy areola. These are usually carried out under local anesthesia. However, we prefer to do a limited liposuction even in thin individuals. The advantages of liposuction include less bleeding, less postoperative discomfort, and improved surgical outcomes.
- Gynecomastia with excess (redundant) skin. These individuals present with sagging breasts. It is usually seen in individuals following massive weight loss. Weight loss over 25 kg leads to such presentations. After a liposuction and gland excision, the skin may have a persistent sagging. In case such an outcome is anticipated, we approach this in two different ways. One, proceed with a reduction of the breast tissue and wait for skin recoil to take effect. The persistence of skin excess after a year is treated with a skin excision procedure. The second involves the removal of the excess skin during the first surgery (gynecomastia correction). The skin removal pattern depends on the severity and extent of the excess skin. It may be removed as a doughnut with a vertical extension, or a vertical with lateral extension. The removal of skin is associated with longer scars when compared to surgery without skin removal. The treatment plan as well as the pattern of skin excision is undertaken on a case-to-case basis. The skin excisional (removal) procedure is usually done under general anesthesia.
What are the differences between local and general anesthesia when used for correction of gynecomastia?
Both local and general anesthesia have relative merits and demerits. We prefer local anesthesia in our practice and reserve general anesthesia for individuals who are anxious or need skin excision. The advantages of local anesthesia for gynecomastia correction include the following,
- Patients can avoid fasting after the procedure.
- Faster recovery. Patients can ambulate soon after the procedure when it is done under local anesthesia.
- Absence of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Some individuals may experience nausea and vomiting with general anesthesia. This is not seen with local anesthesia. Other complications associated with general anesthesia are also avoided when the procedure is carried out under general anesthesia.
- Reduced incidence of collections. We find a reduced incidence of seromas with local anesthesia in our practice.
- Better pain relief during the postoperative period. Under local anesthesia, a higher dose of numbing agents is used during tumescent infiltration before the surgery. The benefits of ensuring complete pain relief during the surgery continue during the early postoperative period.
- Lesser cost. The use of general anesthesia requires more expertise and consumables. Surgical correction under local anesthesia is cheaper when compared to surgery under general anesthesia.
- It takes longer to perform the procedure under local anesthesia. The achievement of adequate analgesia before the surgery takes longer when compared to general anesthesia.
- Local anesthesia may not be suitable for anxious individuals.
Is it possible to undergo secondary (repeat) surgery after a previous gynecomastia correction?
Such corrections are called secondary corrections. These are usually carried out one year after the primary surgery. The reasons for secondary surgery include contour abnormalities, the presence of residual glands, or prominent scars. Patients who present for secondary corrections should have realistic expectations about the procedure. The operative plan for secondary surgery is similar to the primary surgery. We sometimes carry out fat grafting to improve contour abnormalities. The fat harvested during liposuction is injected into deficient areas. We tend to see improved outcomes with a healthy lifestyle and near-ideal body weight.
Why do we treat gynecomastia?
In case an individual is experiencing a sense of shame and embarrassment because of gynecomastia, adequate treatment of this condition leads to an improvement in body image. Patients report improved confidence and self-esteem after a gynecomastia correction.
Related topics.
- Gynecomastia correction under local anesthesia
- Recovering from gynecomastia corrective procedure
- Scars associated with gynecomastia correction
- Late changes following gynecomastia correction
- Asymmetry (difference between the left and right) and its management.
- When not to do gynecomastia surgery?
- Nipple-areola appearance and gynecomastia
- Being overweight with gynecomastia
- Liposuction under local anesthesia
- Shedding weight before liposuction
- Managing excess skin in gynecomastia
- Do I have gynecomastia?
- Secondary corrections for gynecomastia
- Treatment options in individuals with excess skin in gynecomastia
- Why do liposuction in gynecomastia treatment?
- Pain associated with gynecomastia correction
To visit our web page on gynecomastia in Malayalam, please visit: https://www.plasticsurgerymalayalam.com/gynecomastia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
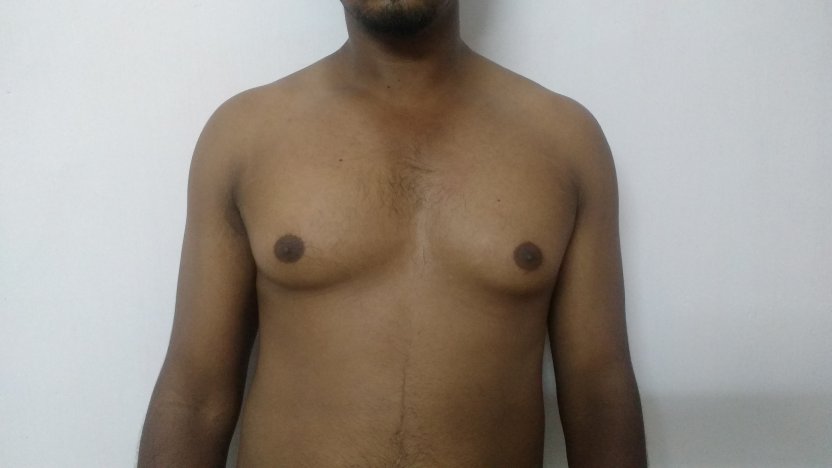
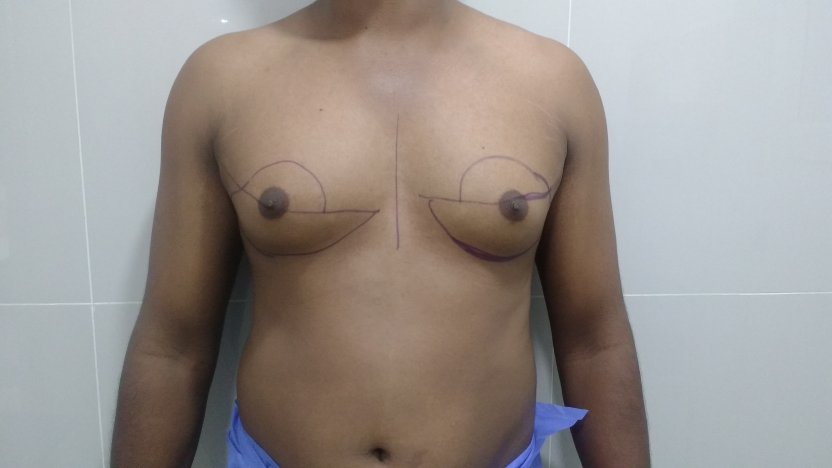
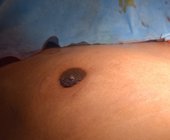
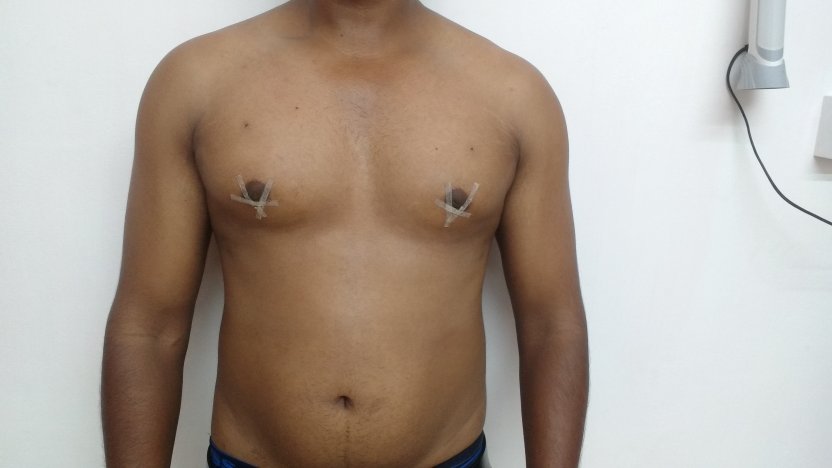
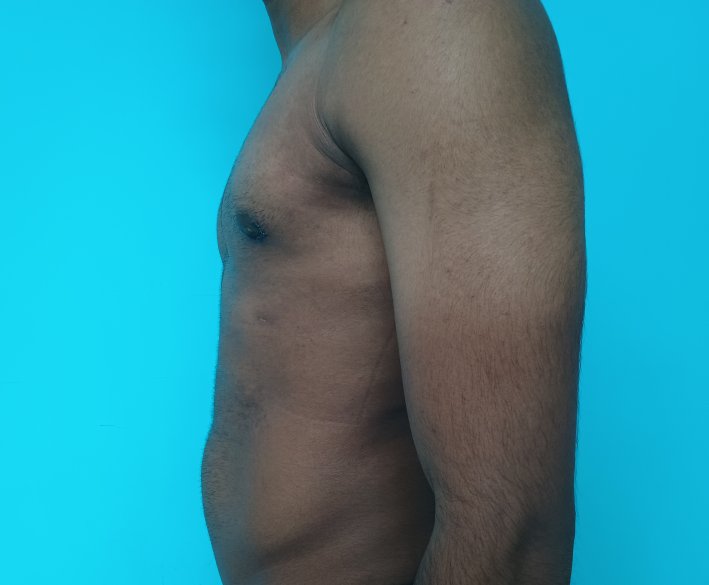
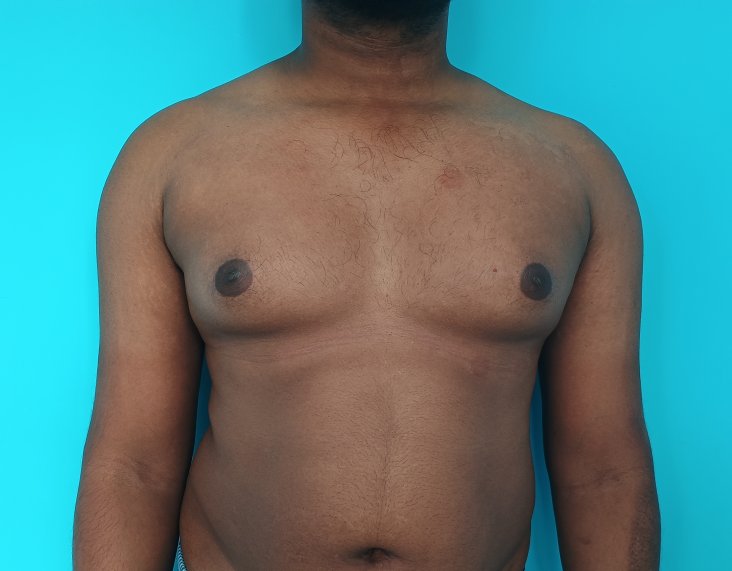
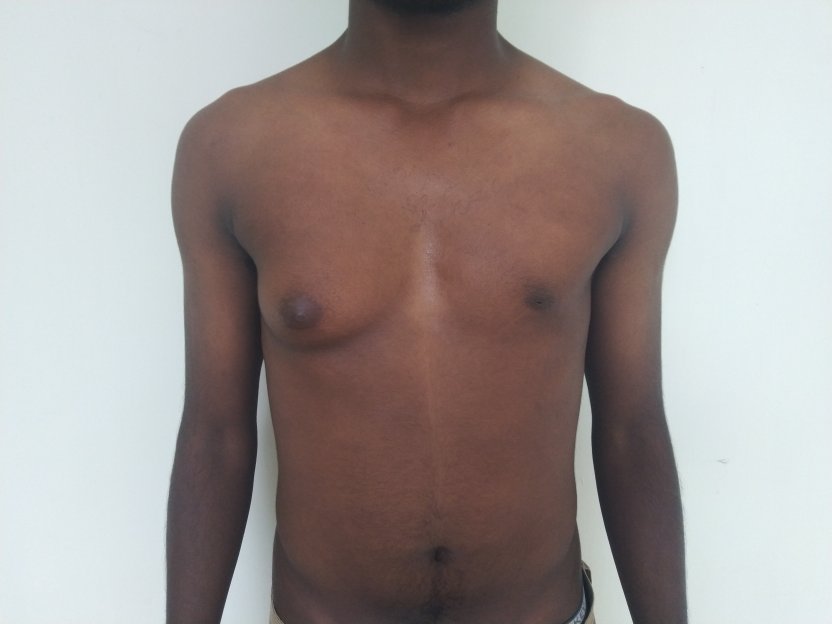
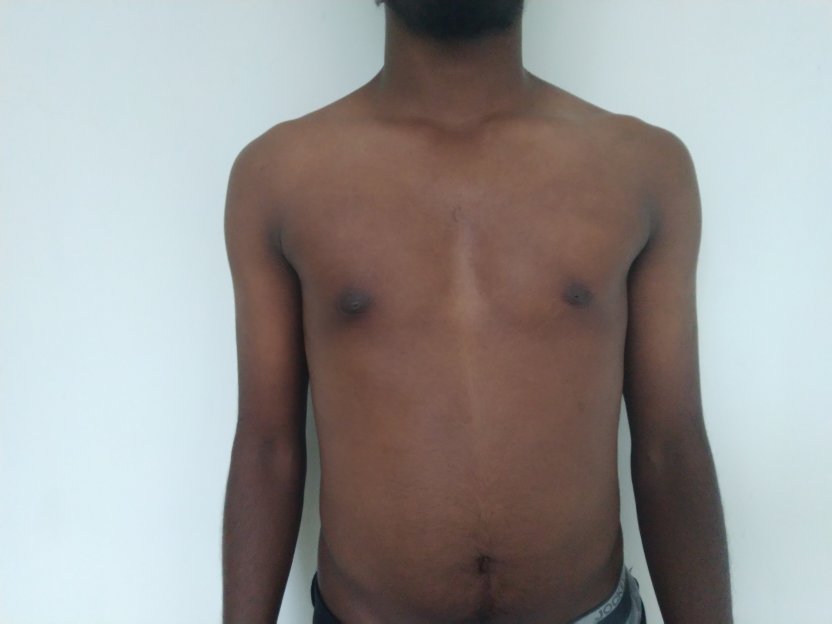
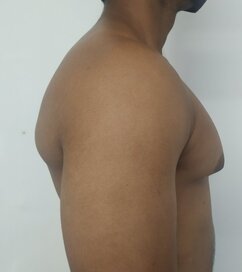
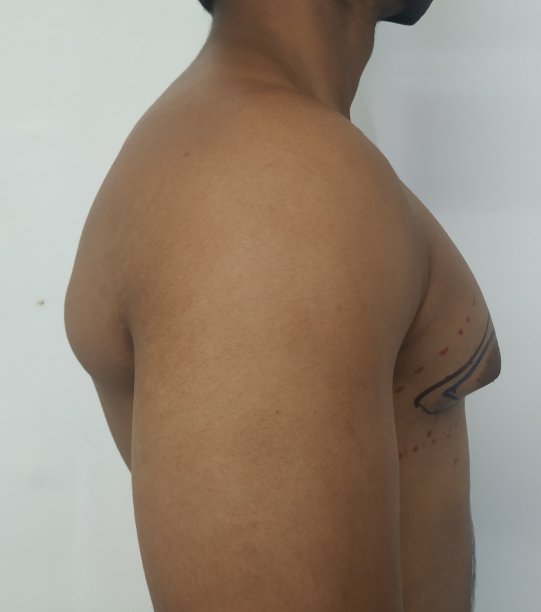
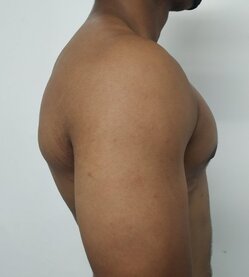
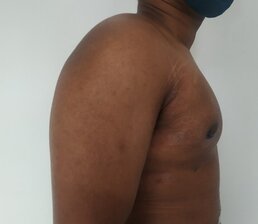
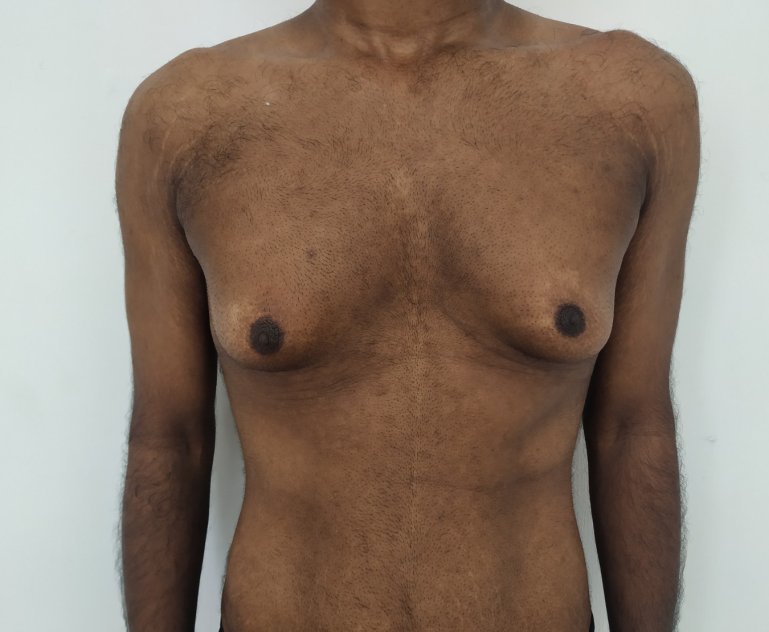
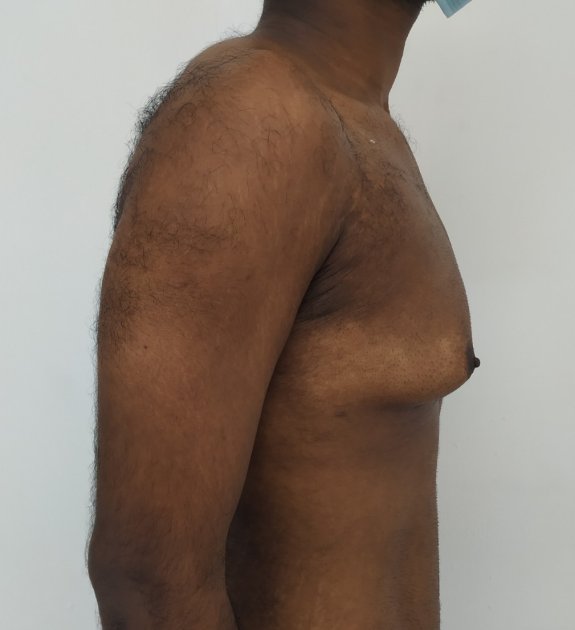
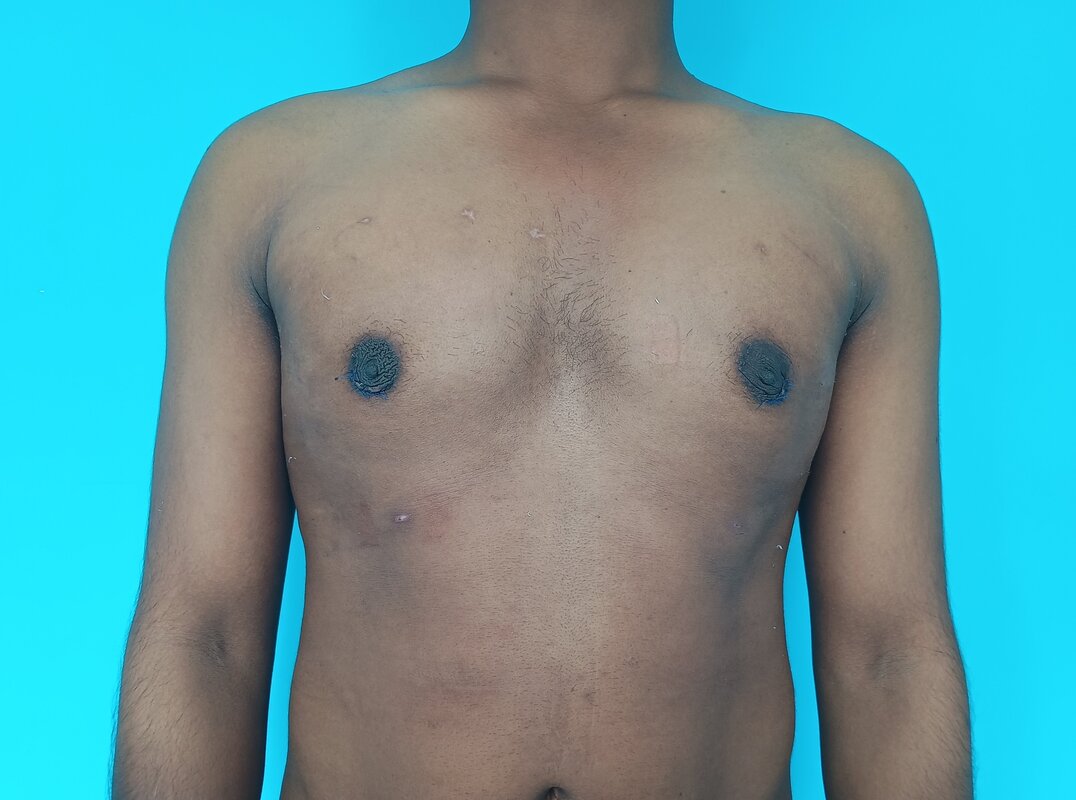
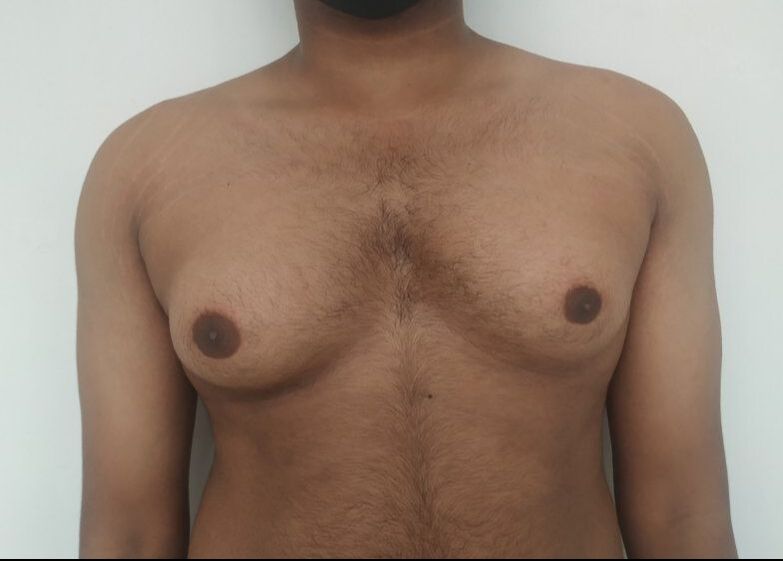
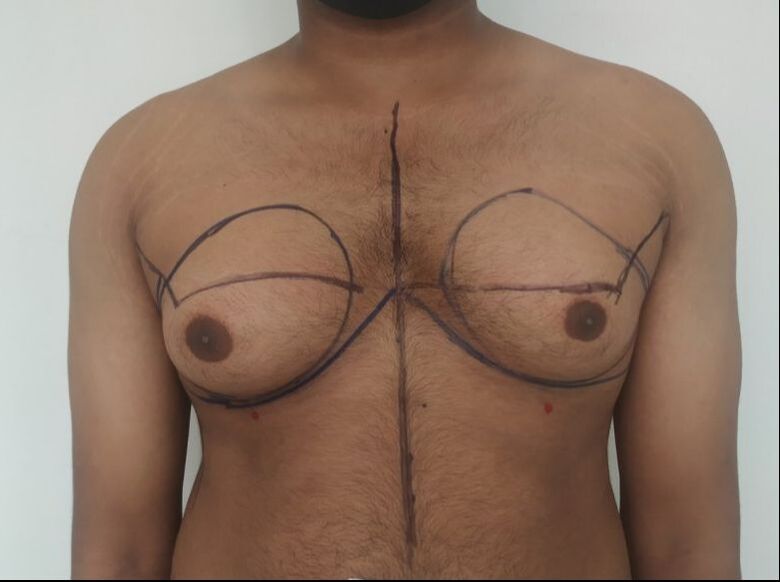
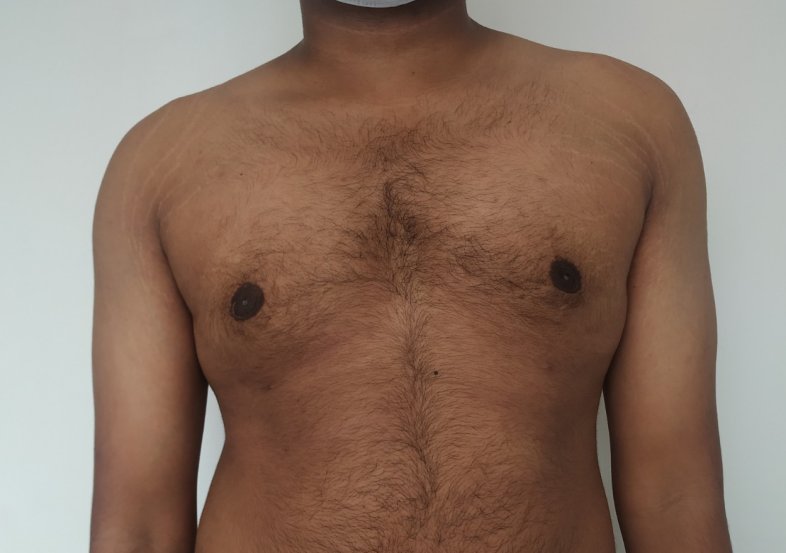
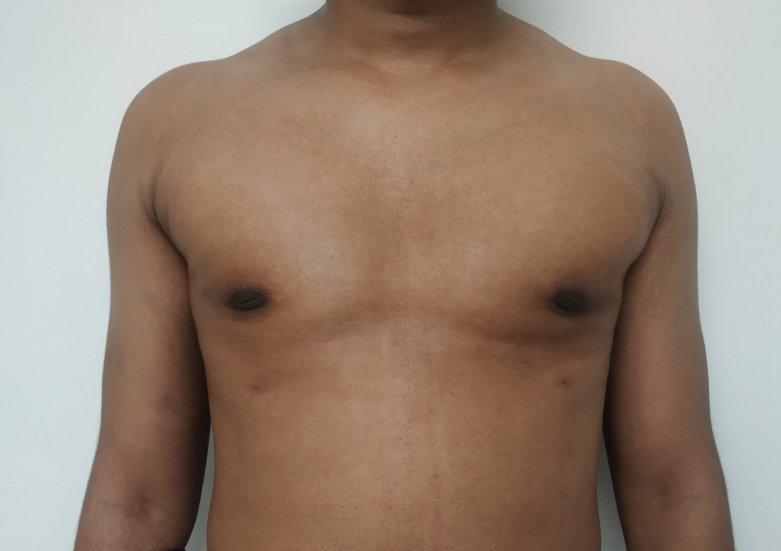
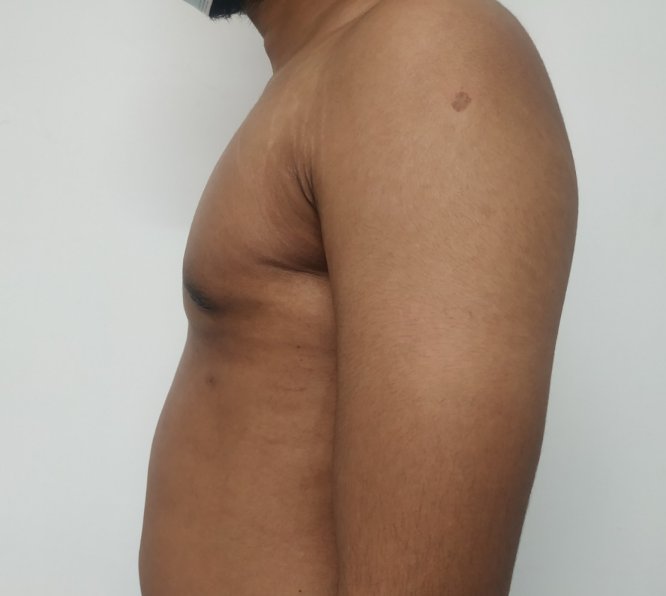
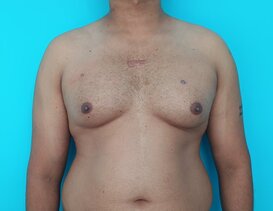
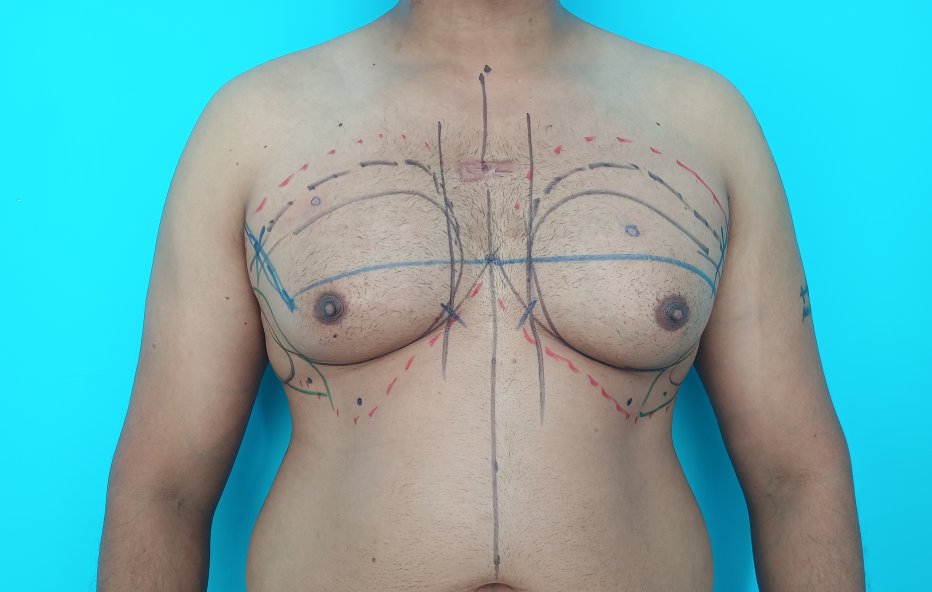
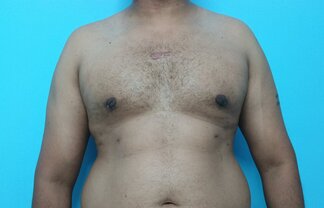
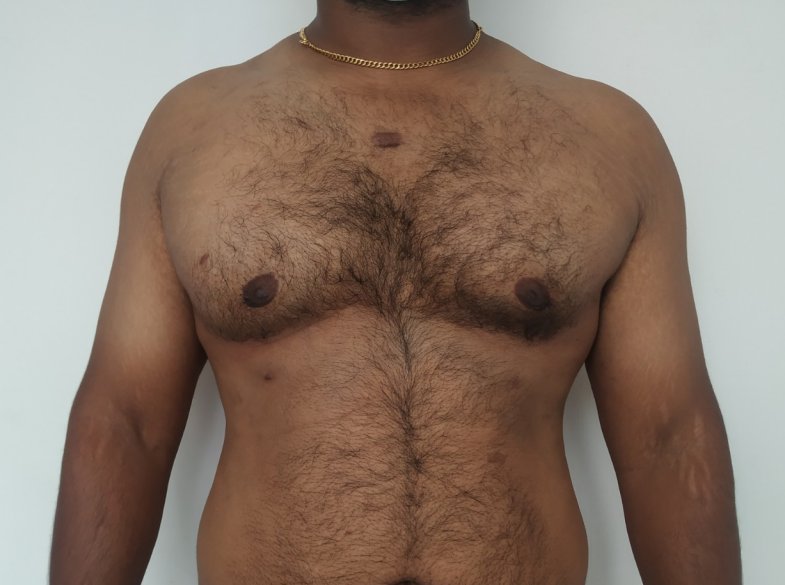
Patient journey: The following images describe a patient journey during gynecomastia correction. Patient underwent liposuction and gland removal with an areolar incision under general anesthesia in a hospital setting. Recovery was uneventful.
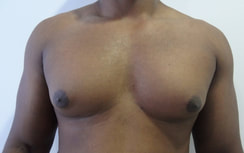
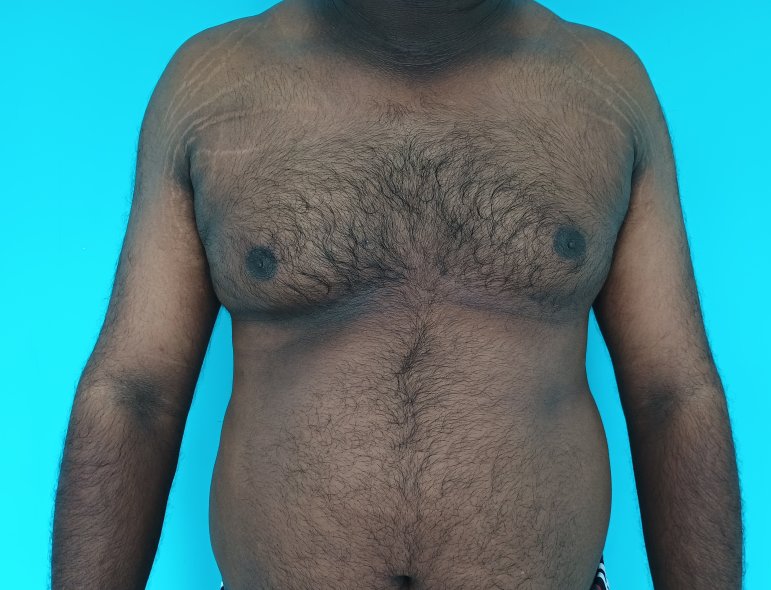
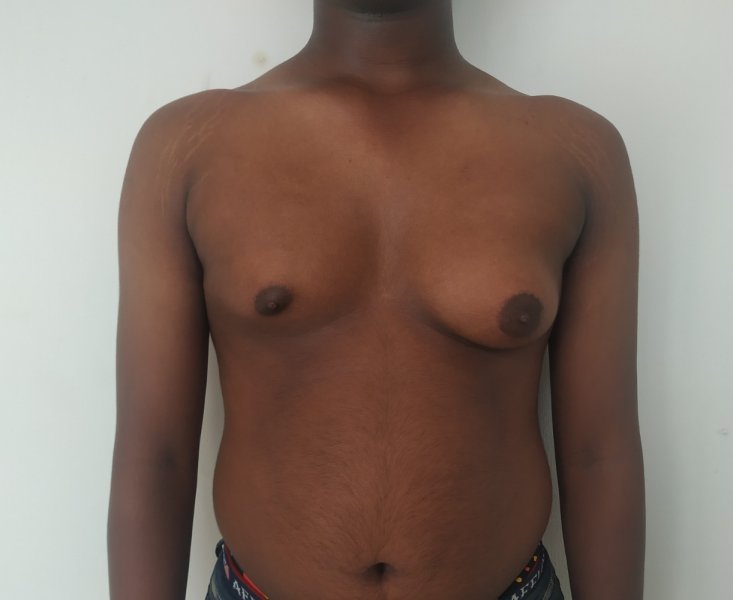
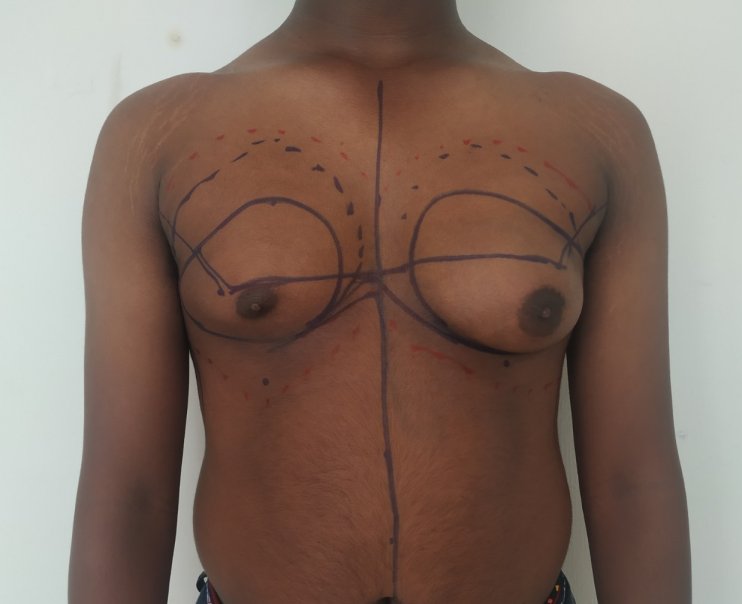
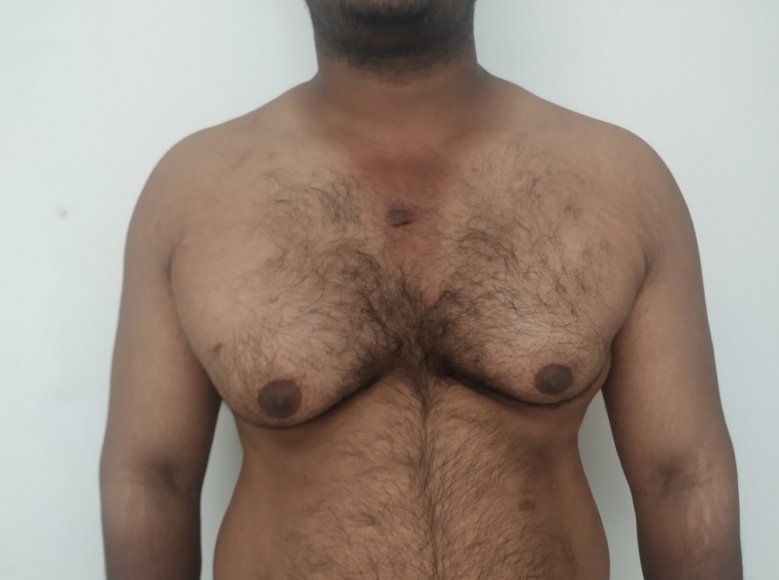
Gynecomastia treated in a muscular individual with direct excision of the gland through an areolar incision. Liposuction was not performed.