Hair transplant | Indications | Types of hair transplant | Steps | Recovery | Ancillary treatments
Hair transplant
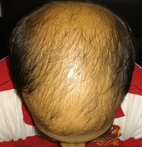
The hair on the top of the head (scalp) frames our face. The loss of hair of scalp leads to an aged appearance and can lead to significant distress among those affected by this condition. Preserving and restoring this part of our body has lead to a very large industry offering various solutions. Hair transplant is a surgical procedure carried to redistribute hair follicles. In this procedure, we move living hair grafts (hair surrounded by a sliver of tissue) from an area of abundance (usually the back of the head) to areas where more hair is desired. Though this procedure has been around for decades, recent years have witnessed technical refinements and more acceptance among hair loss patients. Hair transplant is an outpatient procedure carried out under local anesthesia. This means patients need not be admitted to a hospital once the procedure is over.
Indications
The most common indication for a hair transplant is male pattern baldness. Men with this condition have receding hairline and loss of density of hair of the scalp. The recession (moving back) of the hairline starts at the forehead and progressively extends backward. The time of onset of hair loss and the extent to which it can progress is variable. It means the speed at which hair is lost and the extent to which it will progress (severity of baldness) will be different in individual X when compared to individual Y. Various factors influence male pattern baldness. Male pattern baldness is also known as androgenic alopecia. This is because the hair loss is mediated by the action of a male hormone known as DHT (dihydrotestosterone). The follicles which are prone to male pattern baldness are vulnerable (sensitive) to the effects of DHT. Heredity (inherited) and the role of the environment are also important in male pattern baldness. In short multiple factors play a role in this condition.
Hair loss can also be as a result of other illnesses, trauma etc. Trauma can result in loss of hair either due to direct injury to the hair follicles or as a result of the scarring. Loss of hair in beard, lips, and eyebrow is a common occurrence. The loss of hair adds to the sequelae following the injury. Many of these conditions are treated with hair transplant. Hair transplant is also carried out during male to female sex reassignment surgery to soften the recession along the corners of the forehead. Hair transplant is done to enhance the appearance of a beard or mustache in those who desire a more dense appearance.
Some individuals are good candidates for hair transplant and some are not. Some of the criteria that decide the suitability include,
Since we are redistributing hair from the back and sides of the head, the quality of the grafts is important for a good outcome. The donor hair parameters that affect the outcome include,
Types of hair transplant
The differences in hair transplant techniques arise depending on the type of technique used for harvest of the grafts. The two main techniques are,
The increasing acceptance of FUE also owes to the absence of a linear scar across the back of the head. There is less pain and discomfort when compared to the strip technique. Patients are able to get back to work within 2 days because of the faster recovery.
Steps of hair transplant
The evaluation of an individual for hair transplant begins with a consultation. During the consultation, we assess the expectations relating to the design and position of the new hairline and density of hair follicles. We assess the quality of the donor site.
Laboratory investigations are ordered to diagnose any underlying causes that can lead to hair loss. Laboratory investigations help us to know certain blood parameters which correlate with the healing and recovery from the procedure.
Hair transplant is an outpatient procedure. This means patients are not admitted in the clinic after the procedure. It is carried out under local anesthesia. Hair transplant takes approximately 6 to 8 hours to perform. Duration of the procedure depends on the extent of the procedure. Larger sessions of hair transplant take longer to perform.
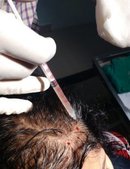
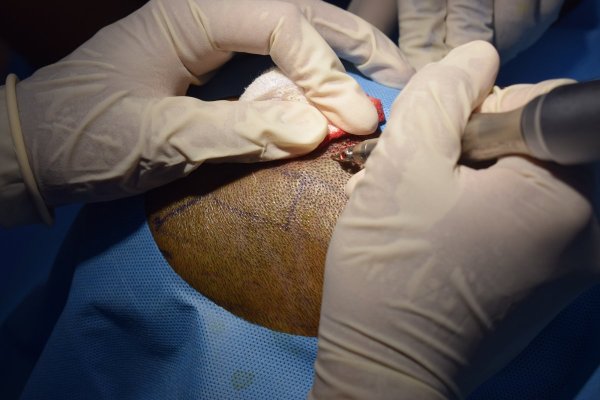
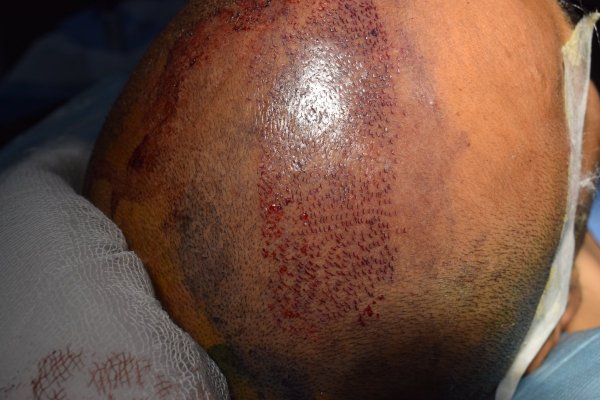
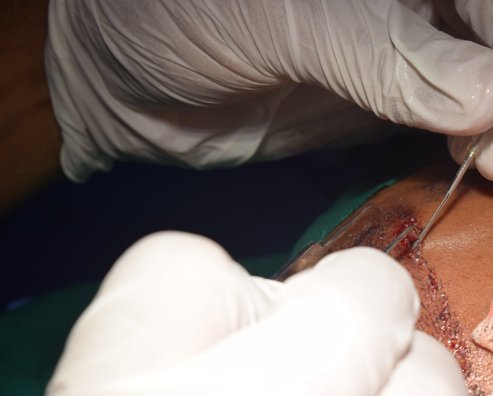
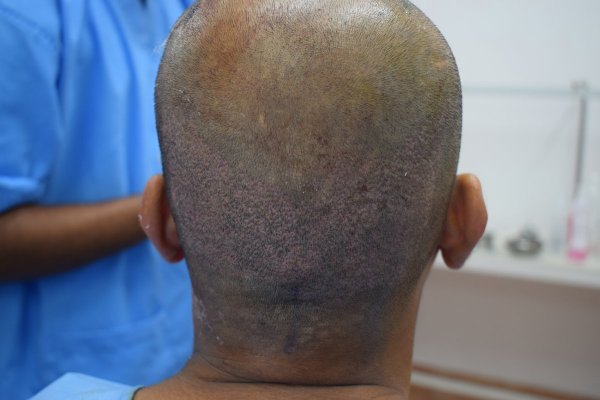
Patients for hair transplant should come for the procedure accompanied by a friend or relative. We advise a light breakfast on the morning of the procedure. We review the donor and recipient sites and the new hairline design before the procedure. Hair is first washed and trimmed to a few millimeters long. The donor area is numbed with local anesthetic. We prefer FUE technique for most of our hair transplants. The donor areas are numbed with a local anesthetic solution. This insures an almost pain-free harvesting of the follicular grafts. The harvesting of the follicular units is performed in a prone (lying with face downwards) position. Frequent breaks are taken to relax the neck and back. Lateral (face turned sideways) position is used for harvesting follicles from the area close to the ears. The harvesting is relatively painless due to the numbing effect of the local anesthetic. The harvested follicles are sorted and collected in small containers with cold saline. Once the required number of follicular units are harvested the donor sites are cleaned and covered with sterile gauze dressing. In FUE, the donor area soon heals due to the small size of the punches. These have usually healed at the first follow-up visit after 2 days. The rapid healing is also contributed by the small size of the punches.
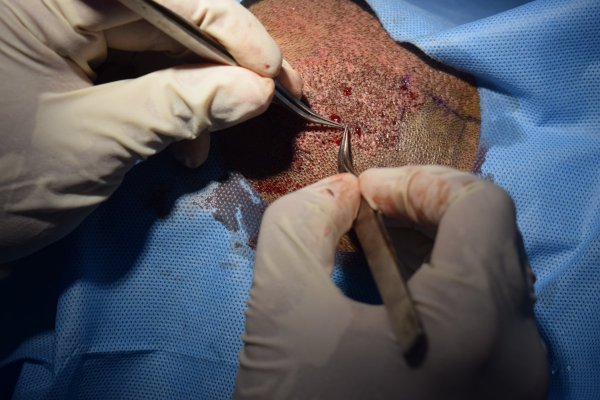
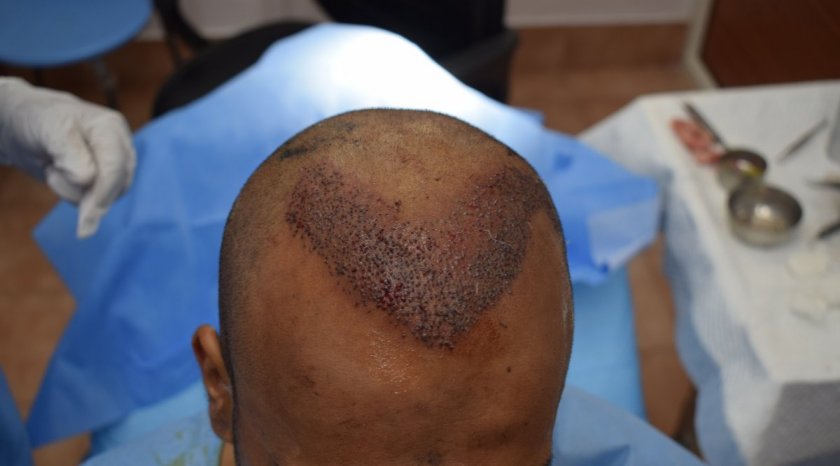
We usually take a lunch break after harvesting. The patient is free to eat and visit the restroom. The next part of the procedure involves implantation (placing the grafts) of the harvested follicles into the bald areas of the scalp. The recipient areas are numbed with the help of local anesthetic solution. Small entry slits are made on the receipt areas with the help of tiny blades. The resulting slits are then filled with the harvested follicles. Once the implantation is complete the recipient area is covered with a tulle and gauze dressing. The patient is instructed about the post-operative care before they leave the clinic.
Recovery following hair transplant
We advise pain medications for a few days. Patients are advised to avoid heavy exertion for 2 weeks following the procedure. It is normal to expect some swelling around the eyes in some patients. This usually resolves over the next few days. Patients are reviewed in the clinic after two days. The dressings are removed and the treated areas are cleansed. The donor sites are usually healed by two days. Patients are given instructions on taking care of the treated areas.
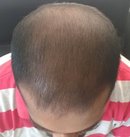
The recipient sites form scabs (crusts) around the new hair follicles. Patients are advised to apply shampoo and pat the area dry after washing it with water. The scabs fall off within the ten days to two weeks after the hair transplant. Patients can appreciate the growth of the transplanted grafts. After a month or so the transplanted hair grafts begin to fall off. This is expected during a normal recovery. Hair begins to grow back after 4 months. The growth keeps improving over the next few cycles. We tell our patients to wait for a year to see the final results of the procedure.
We sometimes stage the hair transplant procedure. Patients may opt to build a hairline and carry out transplant of the posterior parts of the scalp at a later date. The staging also helps to improve the density of a previously treated area. Since the full growth is not seen until one year we recommend any further transplant procedure to be carried out after a year. The staging is sometimes done due to the limited finances of our patients.
Role of ancillary treatment in hair loss patients
Hair loss, especially male pattern baldness is a progressive condition. Various factors influence the progress and final extent of hair loss. It is possible to influence the progression and extent with the help of medicines. The different type of interventions commonly employed include,
Related posts:
1. For more information about PRP, click here.
2. Preventive strategies in the management of hair loss in MPB
3. Hair transplant in donor deficient scalp
The hair on the top of the head (scalp) frames our face. The loss of hair of scalp leads to an aged appearance and can lead to significant distress among those affected by this condition. Preserving and restoring this part of our body has lead to a very large industry offering various solutions. Hair transplant is a surgical procedure carried to redistribute hair follicles. In this procedure, we move living hair grafts (hair surrounded by a sliver of tissue) from an area of abundance (usually the back of the head) to areas where more hair is desired. Though this procedure has been around for decades, recent years have witnessed technical refinements and more acceptance among hair loss patients. Hair transplant is an outpatient procedure carried out under local anesthesia. This means patients need not be admitted to a hospital once the procedure is over.
Indications
The most common indication for a hair transplant is male pattern baldness. Men with this condition have receding hairline and loss of density of hair of the scalp. The recession (moving back) of the hairline starts at the forehead and progressively extends backward. The time of onset of hair loss and the extent to which it can progress is variable. It means the speed at which hair is lost and the extent to which it will progress (severity of baldness) will be different in individual X when compared to individual Y. Various factors influence male pattern baldness. Male pattern baldness is also known as androgenic alopecia. This is because the hair loss is mediated by the action of a male hormone known as DHT (dihydrotestosterone). The follicles which are prone to male pattern baldness are vulnerable (sensitive) to the effects of DHT. Heredity (inherited) and the role of the environment are also important in male pattern baldness. In short multiple factors play a role in this condition.
Hair loss can also be as a result of other illnesses, trauma etc. Trauma can result in loss of hair either due to direct injury to the hair follicles or as a result of the scarring. Loss of hair in beard, lips, and eyebrow is a common occurrence. The loss of hair adds to the sequelae following the injury. Many of these conditions are treated with hair transplant. Hair transplant is also carried out during male to female sex reassignment surgery to soften the recession along the corners of the forehead. Hair transplant is done to enhance the appearance of a beard or mustache in those who desire a more dense appearance.
Some individuals are good candidates for hair transplant and some are not. Some of the criteria that decide the suitability include,
- Good health.
- Non-smokers. Smoking is an important cause of hair loss. Smoking is associated with poorer outcomes. This means a greater likelihood for complications and poorer hair growth.
- Realistic expectations with the procedure. Hair transplant leads to a reasonable increase in density. There are limits to the density in the number of hair follicles which can be transplanted in a square centimeter. Individuals with unrealistic expectations about the procedure are not good candidates for cosmetic surgery.
- Status of the donor area. Since hair transplant involves redistribution of hair follicles from the donor area, reduced donor grafts limit the number of hair grafts that can be distributed into the bald areas. Donor hair depletion can be as a result of advanced male pattern baldness or due to previous donor graft harvesting.
Since we are redistributing hair from the back and sides of the head, the quality of the grafts is important for a good outcome. The donor hair parameters that affect the outcome include,
- Donor density. This refers to the number of follicular units in a given area. A greater number of follicular units (hair grafts) in a given area translates to a greater number of available grafts. Harvesting too many grafts can lead to a moth-eaten appearance at the donor area.
- Type of follicular units. Hair grafts tend to occur in small bunches or clusters. This cluster is referred to as a follicular unit. A follicular unit may contain anywhere from a single graft to four or more hair grafts. During a transplant, a follicular unit is transferred as a single entity. An individual may have varying amounts of hair in follicular units. Some may have a majority of single or 2 hair units whereas some have more of multi-hair follicular units. Transplantation of follicular units with multiple hair grafts leads to a more dense appearance at the recipient site.
- The thickness of the hair. Thicker hair translates into better coverage of the scalp and less visibility of the scalp once the hair starts to grow.
Types of hair transplant
The differences in hair transplant techniques arise depending on the type of technique used for harvest of the grafts. The two main techniques are,
- Strip harvesting. In strip harvest, a strip of skin containing the hair follicles is removed from the side and the back of the head. The resulting wound is closed with sutures. The strip of skin with the follicles is then dissected under magnification outside the body into individual follicular units. These follicular units are then transplanted into the balding areas.
- Follicular unit extraction (FUE). In this technique, small punches are used score and extract individual follicular units. The resulting small wounds heal by itself over the next 2 days. Hence this technique is also referred to as suture-less hair transplant. FUE is a more time-consuming process since individual units are scored sequentially. Unlike strip harvesting technique FUE does not require any extensive graft preparation. It requires a lesser number of operators to accomplish the procedure. FUE has been found to be increasingly popular among patients.
The increasing acceptance of FUE also owes to the absence of a linear scar across the back of the head. There is less pain and discomfort when compared to the strip technique. Patients are able to get back to work within 2 days because of the faster recovery.
Steps of hair transplant
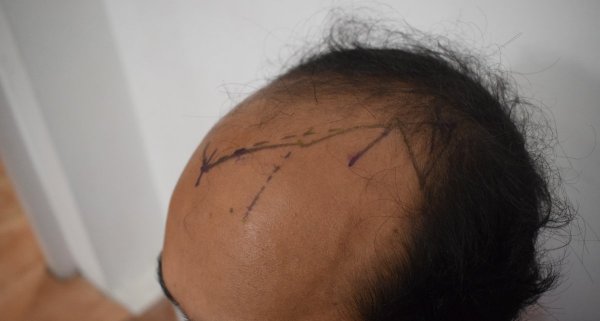
The evaluation of an individual for hair transplant begins with a consultation. During the consultation, we assess the expectations relating to the design and position of the new hairline and density of hair follicles. We assess the quality of the donor site.
Laboratory investigations are ordered to diagnose any underlying causes that can lead to hair loss. Laboratory investigations help us to know certain blood parameters which correlate with the healing and recovery from the procedure.
Hair transplant is an outpatient procedure. This means patients are not admitted in the clinic after the procedure. It is carried out under local anesthesia. Hair transplant takes approximately 6 to 8 hours to perform. Duration of the procedure depends on the extent of the procedure. Larger sessions of hair transplant take longer to perform.
Patients for hair transplant should come for the procedure accompanied by a friend or relative. We advise a light breakfast on the morning of the procedure. We review the donor and recipient sites and the new hairline design before the procedure. Hair is first washed and trimmed to a few millimeters long. The donor area is numbed with local anesthetic. We prefer FUE technique for most of our hair transplants. The donor areas are numbed with a local anesthetic solution. This insures an almost pain-free harvesting of the follicular grafts. The harvesting of the follicular units is performed in a prone (lying with face downwards) position. Frequent breaks are taken to relax the neck and back. Lateral (face turned sideways) position is used for harvesting follicles from the area close to the ears. The harvesting is relatively painless due to the numbing effect of the local anesthetic. The harvested follicles are sorted and collected in small containers with cold saline. Once the required number of follicular units are harvested the donor sites are cleaned and covered with sterile gauze dressing. In FUE, the donor area soon heals due to the small size of the punches. These have usually healed at the first follow-up visit after 2 days. The rapid healing is also contributed by the small size of the punches.
We usually take a lunch break after harvesting. The patient is free to eat and visit the restroom. The next part of the procedure involves implantation (placing the grafts) of the harvested follicles into the bald areas of the scalp. The recipient areas are numbed with the help of local anesthetic solution. Small entry slits are made on the receipt areas with the help of tiny blades. The resulting slits are then filled with the harvested follicles. Once the implantation is complete the recipient area is covered with a tulle and gauze dressing. The patient is instructed about the post-operative care before they leave the clinic.
Recovery following hair transplant
We advise pain medications for a few days. Patients are advised to avoid heavy exertion for 2 weeks following the procedure. It is normal to expect some swelling around the eyes in some patients. This usually resolves over the next few days. Patients are reviewed in the clinic after two days. The dressings are removed and the treated areas are cleansed. The donor sites are usually healed by two days. Patients are given instructions on taking care of the treated areas.
The recipient sites form scabs (crusts) around the new hair follicles. Patients are advised to apply shampoo and pat the area dry after washing it with water. The scabs fall off within the ten days to two weeks after the hair transplant. Patients can appreciate the growth of the transplanted grafts. After a month or so the transplanted hair grafts begin to fall off. This is expected during a normal recovery. Hair begins to grow back after 4 months. The growth keeps improving over the next few cycles. We tell our patients to wait for a year to see the final results of the procedure.
We sometimes stage the hair transplant procedure. Patients may opt to build a hairline and carry out transplant of the posterior parts of the scalp at a later date. The staging also helps to improve the density of a previously treated area. Since the full growth is not seen until one year we recommend any further transplant procedure to be carried out after a year. The staging is sometimes done due to the limited finances of our patients.
Role of ancillary treatment in hair loss patients
Hair loss, especially male pattern baldness is a progressive condition. Various factors influence the progress and final extent of hair loss. It is possible to influence the progression and extent with the help of medicines. The different type of interventions commonly employed include,
- Antioxidants and vitamins. Many studies have shown an increased hair growth following medical therapy. These need to be taken for a prolonged duration for good results.
- Minoxidil lotion. Minoxidil was first introduced as a medicine for the management of high blood pressure. Soon the benefits on the growth of hair were recognized. Minoxidil is prescribed as a topical application. Patients commonly apply it twice daily on their scalp. A minimum contact time is necessary for optimal results. Minoxidil too has to be applied for a prolonged period for patients to get optimal results.
- Finasteride. Finasteride is a medicine which blocks the action of an enzyme which converts testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is responsible for the hormone-mediated loss of hair follicles in male pattern baldness. Finasteride is most effective for hair growth in the vertex. Finasteride carries a good safety profile. However, due to the possibility of side effects some patients opt not to take finasteride. Finasteride is approved by FDA for the management of male pattern baldness.
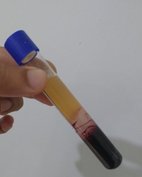
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP). Platelets are small cells found in the blood which play an important role in the arrest of bleeding. Platelets are also rich in chemicals called growth factors. These factors help in improving cell growth. The platelet-rich fraction of the blood concentrates these platelets to a small volume. PRP is obtained from the blood of an individual. The collected blood is processed to give a platelet-rich fraction. This is injected into areas to deliver the benefits of the platelet-derived growth factors. It is a simple outpatient procedure. PRP also finds use in the management of fine wrinkles, pigmentation abnormalities and in sports medicine. The recent popularity of the procedure is probably due to the simplicity and minimal downtime of the procedure. Patients can return back to work or play soon after the PRP treatment.
Related posts:
1. For more information about PRP, click here.
2. Preventive strategies in the management of hair loss in MPB
3. Hair transplant in donor deficient scalp