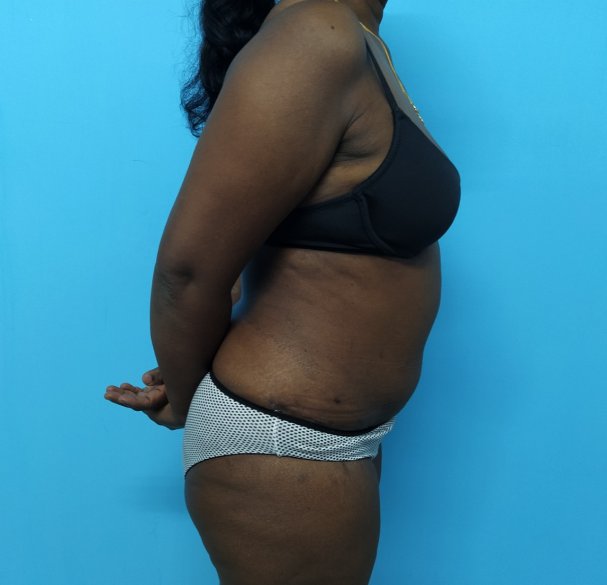
TUMMY TUCK ( ABDOMINOPLASTY )
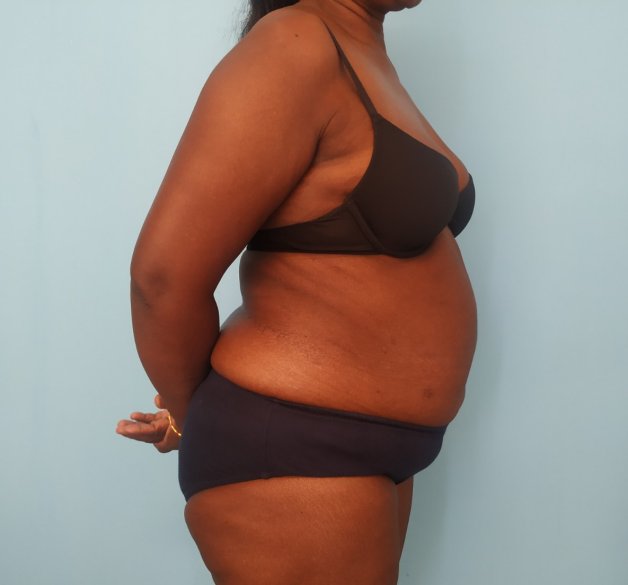
The abdomen comprises the area between the ribs and the pelvis. It is important due to functional and aesthetic reasons. The appearance of the abdomen changes as we age. A youthful-looking abdomen is a sign of health and vitality. An abdominoplasty is a surgical procedure to improve the appearance and function of the abdomen. It is also referred to as a 'tummy tuck'.
What are the aging-related changes in the abdomen?
The abdomen is subject to changes in appearance with aging. In women, the changes are more pronounced due to the effect of pregnancy.
The abdomen is composed of skin, subcutaneous (under the skin) fat, muscles, the fascia surrounding the muscles, and visceral organs. Fat is also seen in proximity to the visceral organs. This fat is referred to as visceral fat. All of these structures change due to aging. These changes reflect in the appearance of the abdomen.
The aging-related changes include the following:
What does an abdominoplasty achieve?
Abdominoplasty can improve upon many of the changes in the skin, subcutaneous fat, and muscle fascia layers. It cannot improve upon the changes due to the deep fat.
Who is a good candidate for abdominoplasty?
The following are good candidates for abdominoplasty.
How is an abdominoplasty done?
It begins with a consultation wherein the patient is examined. The areas of dissatisfaction are evaluated. A clinical examination helps assess the amount of deep fat, muscle fascia laxity, presence of hernias, distribution of subcutaneous fat deposits, and skin laxity. Patients also receive further imaging tests to evaluate the presence of hernias. These are usually carried out in the form of an ultrasound or a CT scan. Those who are good candidates for abdominoplasty undergo further tests in the form of blood investigations, ECG, and a chest x-ray to assess the fitness to undergo the procedure.
Individuals with excess laxity of the muscle fascia layer abdomen are encouraged to wear a tight corset-like binder for a minimum of 2 weeks before the procedure. This helps the individual to better tolerate the changes in the abdominal pressure after abdominoplasty. Patients are also instructed to carry out respiratory exercises with an incentive spirometer starting two weeks before the procedure.
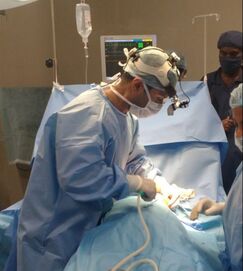
Abdominoplasty is usually carried out under general anesthesia in our practice. Liposuction of the abdominal wall is carried out on the front and sides of the abdomen. Following liposuction, the abdominal skin and the underlying fat are removed from the lower part of the abdomen. The excised skin is in the form of an ellipse with the widest part in the center. The underlying fascia layer is tightened using sutures. The resulting wound is closed in layers. Patients usually have drains exiting the skin below the incision. Drains are small tubes that help drain fluids from the operated areas. These drains are removed during the week after the surgery. The removal of drains is based on the drain output. Patients can easily manage the drains while they are at home.
Patients can move about after recovering from the anesthesia. Early movement helps avoid stasis (collection) of blood in the lower limbs. During the first 10 to 14 days patients have to move with a forward bent at the hips. This helps to reduce the discomfort at the operated site. This discomfort reduces as the tissues become laxer in the following days. They can gradually come back to an erect posture after this period.
Patients can shower from the second day following the surgery. The incision sites have to be covered with a small dressing. The dressings are changed daily by the patient till the wounds have completely healed. This takes approximately 10 days. A pressure garment has to be worn over the dressing. A pressure garment helps reduce swelling, improves healing, and improves outcomes.
Individuals can return to a desk job after about two weeks. Individuals can resume heavy exertion, like lifting weights after about 6 weeks.
How long does one have to stay in the hospital after an abdominoplasty?
We keep the patients for overnight observation after the surgery. Patients can usually go home the next day. Some of our patients choose to extend the hospital stay for one another day.
What are the complications associated with abdominoplasty?
Abdominoplasty when performed in properly selected candidates is associated with fewer complications. The incidence of complications increases with co-existing illnesses and in smokers.
The non-specific complications include the following,
What are the changes that can be expected during a normal recovery following an abdominoplasty?
A patient undergoing abdominoplasty would witness many changes at the operation site in the initial months. These are usually temporary and most of them go away completely. It is important to know about these,
What is neo-umbilicoplasty?
This is a surgical procedure to make a new umbilicus. It is often carried out in an abdominoplasty. The location of the new umbilicus is derived from the position of the neighboring bony landmarks. It is achieved with the help of small incisions, defatting (removal of fat), and anchoring sutures. An aesthetic umbilicus enhances the appearance of an abdominoplasty.
How are the abdominal wall hernias managed?
The type of treatment of these hernias depends on the location and size of the defect (gap) of the abdominal wall. The most commonly seen hernias include a hernia near the umbilicus or those associated with previous surgery like a caesarian section. Hernias near the umbilicus with small defects are closed with the help of sutures. Larger hernias and those associated with a previous incision would usually need the use of a mesh to reinforce the repair. The rest of the steps are similar to those done in patients without a hernia. In some individuals with large hernias, we may stage the repair such that the hernia repair is done during the first surgery and abdominoplasty is carried out during a later operation.
What should an obese or overweight individual do in case they are not considered to be a good candidate for surgery?
The presence of excess visceral fat is associated with poorer outcomes following an abdominoplasty. In case an individual has excess visceral fat, they can reduce the amount of fat with the help of dietary modifications. Bariatric surgery may be indicated in some individuals who do not get relief with dietary modifications. Once an individual can reduce the visceral fat and can maintain a stable weight, they can undergo a body contouring procedure like abdominoplasty.
What are the benefits associated with abdominoplasty?
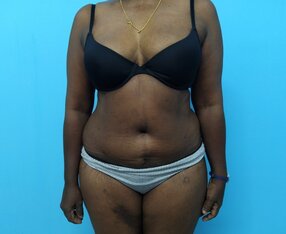
Abdominoplasty is associated with aesthetic and functional improvements in the abdomen. Patients report improved body image.
What are the aging-related changes in the abdomen?
The abdomen is subject to changes in appearance with aging. In women, the changes are more pronounced due to the effect of pregnancy.
The abdomen is composed of skin, subcutaneous (under the skin) fat, muscles, the fascia surrounding the muscles, and visceral organs. Fat is also seen in proximity to the visceral organs. This fat is referred to as visceral fat. All of these structures change due to aging. These changes reflect in the appearance of the abdomen.
The aging-related changes include the following:
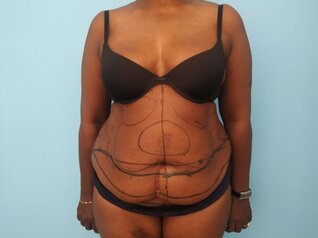
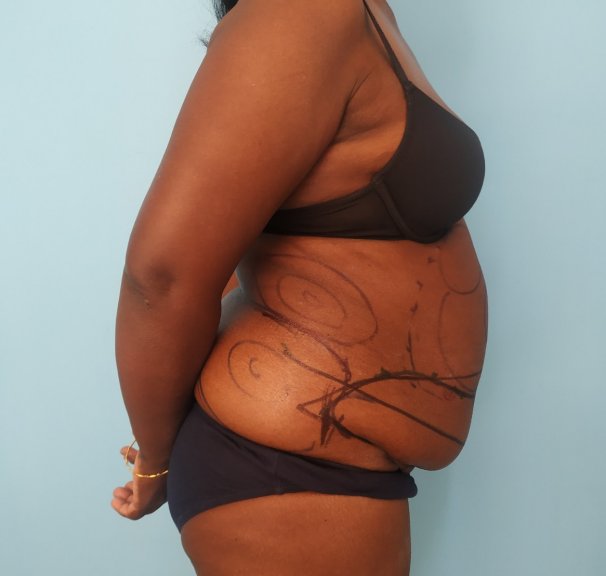
- Skin. Laxity of the skin is first seen in the lower abdomen. As the changes become more severe, the sides and upper abdomen become involved. The skin may show striae. These are usually seen more in the lower abdomen.
- Subcutaneous fat. This is seen as a skin roll that can be pinched between the fingers. The amount of fat increases as a person puts on weight. The increased fat deposition is more evident in the lower abdomen and sides (flanks). In severe cases, patients may have transverse (horizontal) rolls of fat across the torso. These are referred to as pannus. Large fat rolls can make personal hygiene difficult for the affected individual.
- Muscle and fascia. The abdomen is supported by layers of muscles that are surrounded by a layer of tissue called fascia. The fascia becomes lax with aging. There can be a widening of the gap between the vertically oriented muscles in the central part of the abdomen. This is referred to as divarication. The divarication causes the abdomen to be protuberant. Pregnancy can contribute to such changes. Some individuals can have small gaps in the fascia layer through which the structures inside the abdomen like fat and intestine can come to lie in a more superficial position. This is referred to as a hernia. Hernia can be due to preexisting structural weakness or acquired following abdominal surgery.
- Deep fat. Fat is also seen around the visceral organs. This is referred to as intra-abdominal fat. An excess of this fat can result in a protuberant appearance of the abdomen. Increased deep fat is also associated with adverse metabolic changes which can predispose an individual to diabetes and other illnesses. Deep fat is reduced with the help of dietary modifications and in some cases with bariatric surgery.
What does an abdominoplasty achieve?
Abdominoplasty can improve upon many of the changes in the skin, subcutaneous fat, and muscle fascia layers. It cannot improve upon the changes due to the deep fat.
Who is a good candidate for abdominoplasty?
The following are good candidates for abdominoplasty.
- Individuals with good health and no serious comorbidity.
- Nonsmokers.
- Individuals with realistic expectations about the procedure.
- Individuals without excess deep fat.
How is an abdominoplasty done?
It begins with a consultation wherein the patient is examined. The areas of dissatisfaction are evaluated. A clinical examination helps assess the amount of deep fat, muscle fascia laxity, presence of hernias, distribution of subcutaneous fat deposits, and skin laxity. Patients also receive further imaging tests to evaluate the presence of hernias. These are usually carried out in the form of an ultrasound or a CT scan. Those who are good candidates for abdominoplasty undergo further tests in the form of blood investigations, ECG, and a chest x-ray to assess the fitness to undergo the procedure.
Individuals with excess laxity of the muscle fascia layer abdomen are encouraged to wear a tight corset-like binder for a minimum of 2 weeks before the procedure. This helps the individual to better tolerate the changes in the abdominal pressure after abdominoplasty. Patients are also instructed to carry out respiratory exercises with an incentive spirometer starting two weeks before the procedure.
Abdominoplasty is usually carried out under general anesthesia in our practice. Liposuction of the abdominal wall is carried out on the front and sides of the abdomen. Following liposuction, the abdominal skin and the underlying fat are removed from the lower part of the abdomen. The excised skin is in the form of an ellipse with the widest part in the center. The underlying fascia layer is tightened using sutures. The resulting wound is closed in layers. Patients usually have drains exiting the skin below the incision. Drains are small tubes that help drain fluids from the operated areas. These drains are removed during the week after the surgery. The removal of drains is based on the drain output. Patients can easily manage the drains while they are at home.
Patients can move about after recovering from the anesthesia. Early movement helps avoid stasis (collection) of blood in the lower limbs. During the first 10 to 14 days patients have to move with a forward bent at the hips. This helps to reduce the discomfort at the operated site. This discomfort reduces as the tissues become laxer in the following days. They can gradually come back to an erect posture after this period.
Patients can shower from the second day following the surgery. The incision sites have to be covered with a small dressing. The dressings are changed daily by the patient till the wounds have completely healed. This takes approximately 10 days. A pressure garment has to be worn over the dressing. A pressure garment helps reduce swelling, improves healing, and improves outcomes.
Individuals can return to a desk job after about two weeks. Individuals can resume heavy exertion, like lifting weights after about 6 weeks.
How long does one have to stay in the hospital after an abdominoplasty?
We keep the patients for overnight observation after the surgery. Patients can usually go home the next day. Some of our patients choose to extend the hospital stay for one another day.
What are the complications associated with abdominoplasty?
Abdominoplasty when performed in properly selected candidates is associated with fewer complications. The incidence of complications increases with co-existing illnesses and in smokers.
The non-specific complications include the following,
- Infection. It is an uncommon complication. The incidence is higher in those with severe diabetes and smokers. The chances of infection are reduced with the help of antibiotics. Also, we do not combine abdominoplasty with bowel surgery or a hysterectomy to avoid contamination with the luminal contents. It helps reduce the incidence of infection.
- Seromas and hematomas. This can be a result of extensive dissection done in abdominoplasty. With newer techniques like TULUA abdominoplasty the incidence of seromas has been reduced further. Seromas are usually managed conservatively with needle aspiration. They usually settle without any intervention.
- Prominent scars. The scars are usually placed in the fold in the lower part of the abdomen and can be hidden with an undergarment. Some individuals who are prone to get prominent scars would need further care in the form of silicone sheets, pressure garments, and sometimes intralesional injections of steroids. However, in the majority of individuals, these scars settle well.
- Wound healing problems. Delayed healing can be secondary to impaired perfusion (blood supply) of the abdominal wall. It is seen more in individuals with co-morbidities and smokers. This is observed in the postoperative period as delayed healing and wound breakdown. The abdominal (upper) flap in the central part of the incision is the most prone area to get this complication. In case an individual develops wound healing problems, it is usually managed conservatively with repeated dressing changes till the wound heals. Any secondary correction can be carried out after the scar matures. With the newer types of abdominoplasty, there is very less incidence of such complications.
- Venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. This is a very serious but extremely uncommon complication seen in certain types of surgery. Strategies like the frequent passive movement of the lower limbs and early ambulation help reduce the incidence further.
- Visceral (deep abdominal organ) injury. It is an extremely uncommon complication in abdominoplasty. With safer techniques and preoperative screening for hernias, the incidence of such events is reduced.
- Contour abnormalities. This may be seen as part of normal healing in the initial months. They usually settle with time. Contour abnormalities persisting after a year may need further corrective procedures.
- Dissatisfaction with the outcome. The presence of a lot of visceral fat and circumferential laxity of the torso may not be adequately improved with an abdominoplasty. Abdominoplasty is usually not performed in individuals with excess visceral fat. In case an individual has excess visceral fat, it should be reduced before an abdominoplasty. In individuals with circumferential laxity of the torso, a more extensive operation like total body lift (TBL) would be a more appropriate operation.
What are the changes that can be expected during a normal recovery following an abdominoplasty?
A patient undergoing abdominoplasty would witness many changes at the operation site in the initial months. These are usually temporary and most of them go away completely. It is important to know about these,
- An altered sensation of the lower abdomen. These sensations usually recover over months. Because of this patients should avoid using a hot water bottle in the lower abdomen in the initial months following an abdominoplasty
- Feeling of tightness and discomfort when turning. This is due to the surgical tightening of the muscle fascia layer. They settle with time.
- Swelling. This is a normal part of healing following any type of surgery or liposuction. It settles without any intervention. The use of pressure garments helps in a faster resolution of the swelling.
What is neo-umbilicoplasty?
This is a surgical procedure to make a new umbilicus. It is often carried out in an abdominoplasty. The location of the new umbilicus is derived from the position of the neighboring bony landmarks. It is achieved with the help of small incisions, defatting (removal of fat), and anchoring sutures. An aesthetic umbilicus enhances the appearance of an abdominoplasty.
How are the abdominal wall hernias managed?
The type of treatment of these hernias depends on the location and size of the defect (gap) of the abdominal wall. The most commonly seen hernias include a hernia near the umbilicus or those associated with previous surgery like a caesarian section. Hernias near the umbilicus with small defects are closed with the help of sutures. Larger hernias and those associated with a previous incision would usually need the use of a mesh to reinforce the repair. The rest of the steps are similar to those done in patients without a hernia. In some individuals with large hernias, we may stage the repair such that the hernia repair is done during the first surgery and abdominoplasty is carried out during a later operation.
What should an obese or overweight individual do in case they are not considered to be a good candidate for surgery?
The presence of excess visceral fat is associated with poorer outcomes following an abdominoplasty. In case an individual has excess visceral fat, they can reduce the amount of fat with the help of dietary modifications. Bariatric surgery may be indicated in some individuals who do not get relief with dietary modifications. Once an individual can reduce the visceral fat and can maintain a stable weight, they can undergo a body contouring procedure like abdominoplasty.
What are the benefits associated with abdominoplasty?
Abdominoplasty is associated with aesthetic and functional improvements in the abdomen. Patients report improved body image.