|
Liposuction is among the more popular procedures done by a plastic surgeon. Liposuction is carried out as a single procedure or in combination with other surgical procedures. Some individuals refer to it as the 'keyhole' surgery for gynecomastia.
Liposuction has certain advantages over open or conventional surgery. These include small incisions, faster recovery, and less postoperative discomfort. Liposuction can be carried out both under general or local anesthesia. Doing liposuction under local anesthesia has certain benefits. So, what are these benefits? The important ones include,
Are there any differences in technique with liposuction under local anesthesia? There are a few differences. Firstly, the patient is awake, and the monitoring of the patient is simple. When done in an awake patient, it takes longer to complete the procedure. There are a few reasons for this. The initial infiltration of the anesthetic solution in the treatment areas is done in multiple steps and takes longer to complete. Also, we prefer the use of smaller cannulas for infiltration and fat aspiration (suction). We usually use cannulas of sizes 3 mm or below in an awake individual. Due to the smaller cannulas, the aspiration of fat takes more time to complete. Liposuction in the awake individual is more gentle. Who is the right candidate for liposuction under local anesthesia? Almost all candidates for the procedure under general anesthesia are also good candidates for the procedure to be carried out under local anesthesia. However, if the patient is very anxious or has a fear of needles they may not be a good candidate for local anesthesia alone. Such individuals would be better suited for general anesthesia. To summarize liposuction, in awake patients has a better safety profile. It has the added benefits of a faster recovery, and this also makes it suitable as an outpatient procedure. For more information about liposuction click here. Pressure sores tend to occur in bedridden individuals. It is more common among the elderly, though persons of any age can get affected. Pressure sores could be as a result of spinal injury or any prolonged debilitating illness. It is a cause of increased stress in the affected individual and caregivers. It results in increased medical expenses.
Proper care can help us reduce the incidence (prevent) and achieve early healing of pressure sores. The following three aspects form an important part of care among individuals at risk of developing a pressure sore:
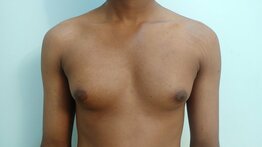
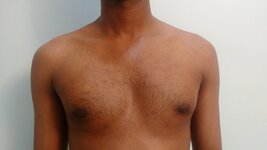
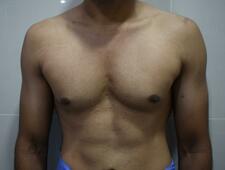
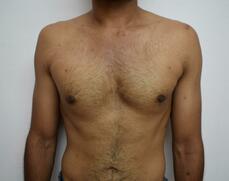
The onset of a skin breakdown must be viewed seriously. It may not be possible to eliminate all of the risk factors that can lead to a pressure sore. However, with adequate care, it is possible to prevent this condition. You can learn more about pressure sores here. Patients with gynecomastia have increased gland in addition to the fat. Fat is found both within the glandular tissue and immediately underneath the skin. Fat in both these places contributes to the deformity. In an overweight individual, the proportion of fat is more than that of a person with ideal body weight. During the surgical correction, fat is removed with the help of liposuction. Small cannulas are introduced under the skin and fat is removed with the help of suction combined with repeated movements of the cannula. Removal of fat leads to an improvement in the contour.
Prolonged and severe gynecomastia is also associated with excess skin. In most individuals removal of the breast tissue leads to the recoil of the skin during the months following surgery. However, in certain individuals, this recoil may not be complete. We may have to perform additional skin excisional procedures to improve the contour in such cases. Individuals with excess weight should try to reduce weight by non-surgical methods. This involves dietary and lifestyle modifications. There are many advantages to doing so. It leads to better postoperative outcomes with more pleasing results. This is in addition to the other health and psychological benefits. Operating in a near-ideal bodyweight individual also means a simpler and shorter surgery. There is a lesser chance of wound-related adverse events such as infection and prolonged healing. BMI or body mass index is commonly used to assess the weight in comparison to the height of the individual. We usually discourage operations on individuals with a BMI greater than 30. Being overweight increases the deformity associated with gynecomastia. However, it is possible to give a good outcome with surgical correction in conjunction with the appropriate lifestyle and dietary changes. Visit here, to learn more about gynecomastia. Gynecomastia is a commonly seen condition among young men. It presents as fullness near the nipples that give a feminine appearance to the male chest.
A very frequently mentioned symptom among such individuals is the appearance of the nipple and the surrounding pigmented skin (areola). Other than the fullness, the appearance seems to look worse when exposed to warmth and improves when exposed to cold or mechanical stimulation. A certain part of the consultation is usually devoted to an explanation of this phenomenon. The pigmented skin surrounding the nipple has radially (like spokes of a wheel) oriented smooth muscles in the skin. Exposure to cold and mechanical stimulation leads to a contraction of these smooth muscles and a resulting contraction of the skin (areola). When the smooth muscles are relaxed the areola tends to look globular. The globular appearance of the areola is considered to be less aesthetic. The presence of smooth muscles in the skin should not be confused with the skeletal muscles situated in a deeper plane. Similar smooth muscles are also found in the scrotum and react in a similar way to variations in temperature and mechanical stimulation. The presence of smooth muscles in the nipple-areola is normal. It is found in everyone. In individuals with gynecomastia, the presence of glandular tissue makes the nipple-areola region more prominent. It also makes the above-mentioned changes in appearance due to the smooth muscle activity more prominent. But that does not mean that the variations as a result of the smooth muscle activity are abnormal. Gynecomastia surgery is undertaken for improvement in the appearance of the male chest. With the removal of the excess breast tissue, the prominence of the nipple-areola is reduced. As the areola is no longer stretched out due to the glandular tissue, the changes of the overlying skin are also significantly reduced. As in other cosmetic surgical procedures, this can also lead to a better body image and more self-confidence. To learn more about gynecomastia visit, www.amicusclinic.in/gynecomastia Gynecomastia is a relatively common condition that can affect men of all ages. It may result in significant mental distress in those affected by it. A frequently asked query is regarding the necessity to undergo surgical correction of gynecomastia. Usually, gynecomastia is a benign condition. As in most cosmetic surgical procedures, the desired outcome is an improvement in appearance and body image. Hence, gynecomastia surgery is most beneficial in those who are distressed by this condition.
In other words, the surgery may not be indicated in those who are not affected by the appearance. Uncommonly gynecomastia can be a result of some other pathology. These can be ascertained by clinical examination and blood tests. In such situations, it may be necessary to ascertain the cause of gynecomastia. Because of this, we recommend the medical screening of gynecomastia. The treatment to undertake any cosmetic surgical correction is a personal one. It has to be arrived at after proper consideration of the possible outcomes, recovery, and complications. A + B = C. So C - B = A. This may apply to simple arithmetic, but things get a bit complex when we are dealing with weight gain and weight loss.
We store our excess energy in the form of fat. Excess calories we may have acquired from our diet. This excess of fat gets stored in our body as fat deposits in different locations. Fat immediately under the skin can be pinched. This layer of fat is found between the skin and muscles. This is also the layer that can be removed with liposuction. Fat also gets stored deep inside our body, close to our internal organs. This is visceral fat. We can neither pinch this fat nor get it removed with plastic surgery. A proper diet can help us get back to our ideal body weight. In some situations, bariatric surgery achieves the same end. However, a prolonged period of increased fat has effects beyond the fatty tissue. It stretches out the overlying skin. Visceral fat also stretches out the fascial layer. This layer is closely associated with the abdominal muscle layer. When we lose fat, the size of the fatty layer reduces. This may be dramatic in cases of severe weight reduction as with weight loss (bariatric) surgery. The stretched out skin and fascia may not get back to the dimensions before the weight gain. As a result, individuals end up with loose folds of skin. To improve this appearance, we have to surgically remove the excess folds of skin. These surgeries are together clubbed under body contouring procedures. We usually wait for a year or more for the weight to stabilize and allowing the skin to recoil by itself before attempting any skin correction. The same approach is used for different body parts, arms (brachioplasty), abdomen (abdominoplasty), thighs (thighplasty) and torso (body-lift). The presence of stretched out skin and fascia is the reason why liposuction may not be the right procedure for abdominal fat. Liposuction can't do much to tackle the laxity of skin and underlying abdominal fascia. With liposuction alone, we may worsen the skin laxity of the abdomen resulting in an increase in loose folds of skin after the procedure. The same line of reasoning is applied to individuals who present for a reduction in the size of arms. We undertake it in two stages, with the first being deflation with diet or liposuction and a second stage with the removal of loose folds of skin. To conclude, we have to tackle the laxity of skin and deeper fascia in cases of weight loss following periods of excess weight gain. These may have undergone irreversible changes. Treatment of such deformities often requires the management of tissues like skin and fascia with the help of body contouring procedures. Such an approach helps us to optimize aesthetic outcomes. Visit the following to learn more, 1. Liposuction 2. Brachioplasty 3. Abdominoplasty In this age, it is almost essential to look lean and fit. Lean is associated with health and vitality. It is common knowledge that a large waistline is contributed by excess fat deposits. And because of this many individuals turn to plastic surgery for liposuction as a solution to this problem. However, all cases of the protuberant belly cannot be tackled by plastic surgery.
Excess deposits of fat can be found in many places within the abdomen. They are found in the layer between the skin and the muscles of the abdominal wall. This is the layer that can be pinched between the fingers as a roll. Fat is also deposited deep inside the muscle layer. This fat is referred to as visceral fat and is found in association with our gut and the area behind it. Other than fat deposits, laxity of the abdominal wall can contribute to protuberance. Laxity of the abdomen can be seen as a result of changes due to aging and pregnancy. A separation of the abdominal muscles in the midline, known as divarication is often seen in such individuals. Some of the above-mentioned deformities can be tackled with the help of plastic surgery. The modalities used for correction include procedures such as liposuction and abdominoplasty. Liposuction involves suction of fat with the help of small cannulas inserted through the skin. Fat is aspirated with the help of a vacuum producing device. Advantages of this procedure include the treatment of relatively large areas with the help of tiny incisions. Patients usually recover fast and are ambulant as soon as they are awake from the effects of anesthesia. It does not involve a prolonged stay in hospital. Liposuction targets only fat that is superficial to the abdominal muscles. We are not able to access the deep or visceral fat with liposuction. Another limitation of liposuction is that it does not address the laxity of the abdominal wall or skin. Abdominoplasty translates into reshaping the abdomen. During an abdominoplasty, we tighten the layer of the muscles. This helps tackle the laxity of the muscle layer. Liposuction is often carried out as a part of abdominoplasty. Liposuction is used to reduce the fat deposits on the flanks and in the upper abdomen. This improves the appearance and increases the safety of the procedure by limiting the areas of surgical dissection. We also reduce the excess skin as an ellipse from the lower abdomen. The rest of the skin is draped to result in a tighter-looking abdomen. As with liposuction, abdominoplasty can't address the visceral fat. A clinical examination helps reveal the cause of the deformity and arrive at a treatment plan. Ideal candidates for both the procedures include patients close to their ideal body weight. They should be non-smokers and have reasonable expectations about the procedure. It is also important to be aware of what can be achieved using plastic surgery. We can achieve a reduction in the fat deposits that are external to the muscles and obtain a tightening of the muscle-fascia layer and skin. Plastic surgery does not address the visceral fat. And because of this, patients need to adopt a dietary and exercise regimen to maintain appropriate levels of visceral fat. Macromastia or disproportionately enlarged breasts in females is not an uncommon condition. Treatment is often sought for physical and mental effects of this condition. Symptoms due to the heavy breasts include shoulder and neck pain, grooving of the skin due to garments and, maceration of the skin under the breast folds. Patients are often embarrassed due to this condition and find difficulty in getting suitable clothes.
Reduction mammaplasty (breast reduction surgery) is a very effective procedure to address macromastia. It helps patients to achieve a reduction in the size of the breasts as well as an improvement in the appearance of the breasts. It also allows us to tackle mild breast asymmetries and help position the nipple and areola to a more aesthetic position. When the procedure is carried out in a patient previously operated for macromastia, it is known as secondary reduction mammaplasty. The following may be some of the reasons to carry out a secondary breast reduction surgery. Patients sometimes report that the breasts have increased in size after the first surgery and desire a further reduction in the size of breasts. They may be bothered about the scars associated with the previous surgery. In certain situations, patients may want to improve the position of the nipple in relation to the rest of the breast. The decision to explore a secondary breast reduction procedure is taken after careful discussions with the patient. Some of the important points factored into the decision making include, the time elapsed after the first surgery, the type of reduction carried out previously, scarring tendency of the individual, etc. The procedure is usually carried out as a short stay procedure in a hospital setting under general anesthesia. Post-procedure patients have to comply with the use of pressure garment and care of the breasts. In cases of secondary correction, patients are usually very familiar with the process of recovery. Breasts are an important part of the body image of a woman. Disproportionately large breasts result in significant morbidity among some of the affected individuals. Reduction mammaplasty is a powerful technique to help those affected by this condition. Click here for more details about reduction mammaplasty. Gynecomastia is an enlargement of the male breast tissue. This enlargement can be of one or both sides. In cases of bilateral involvement, one side can be affected more than the other, leading to an asymmetrical appearance. Mild cases of asymmetry are common. But in certain cases, the difference between the two sides can be readily noticeable. The asymmetry can be as a result of two causes, namely, a difference in the amount of breast tissue or changes as a result of the underlying chest wall and muscles. The treatment strategies for managing the asymmetry depends on the underlying cause. Usually, the reason is apparent during a clinical examination. In the case of asymmetry arising due to the difference in the size of the breast tissue, the treatment involves liposuction and direct glandular excision. We take care to leave behind equal amounts of subcutaneous tissue at the end of the procedure. A more enlarged gland will require a longer time for adequate skin recoil. Such a gland may also have a longer duration of postoperative firmness. In most cases, adequate symmetry is achieved with the passage of time. In cases of asymmetry due to underlying chest muscles, unfortunately, nothing much can be done to correct the difference at the time of surgery. We bring this to the notice of the patient during the consultation. Usually, such differences in chest muscles arise from altered posture and position during strength training exercises. It is recommended that individuals seek help and guidance from an expert physical trainer for the correction of the posture and technique. Gynecomastia surgery is essentially a cosmetic procedure and the goal of undertaking a correction is to minimize the effect of the deformity. Wide variations occur in the presentation of this condition. Asymmetry is a commonly seen variant, even though severe asymmetry is uncommon. In cases of asymmetry, it is important that individuals understand the reason and the role of different treatment strategies to tackle the same. For more information about gynecomastia and related topics, click here. An individual with asymmetry due to difference in the size of the gland. The right side is bigger compared to the left. Asymmetry due to the difference in the size of the underlying muscles. The left pectoralis major is more developed when compared to the right.
Macromastia is a condition with disproportionately enlarged breasts in women. This can be a cause for significant emotional and physical distress in those affected by this condition. Reduction mammaplasty is a surgical condition to reduce the size of the breasts by making it more proportionate to the rest of the body.
The cause of macromastia is usually undetermined. It can be as a result of a change in levels of hormones and sensitivity of the tissues to hormones. There can be an enlargement of the gland, fat and excess skin in this condition. Medicines do not have a significant role in the treatment of macromastia. Surgery is the mainstay of treatment of this condition. Macromastia can result in physical symptoms such as neck and backache, skin grooving and skin rashes over the folds below the breasts. Patients may find it difficult to perform strenuous exercise and other physical activity. Individuals with this condition also find it difficult to get appropriately sized clothing. Macromastia can result in emotional distress and a feeling of embarrassment and social inhibition. Surgical correction is achieved by reduction mammaplasty. This is aimed at reduction of the size the breasts, and reshaping it to give a more pleasing appearance. The areola (pigmented skin around the nipple) is also reduced in diameter in case they are enlarged. The scars associated with this procedure are confined to the skin at the junction between the areola and breast and a vertical limb towards the undersurface of the breast. In most individuals, the scars settle well. Reduction mammaplasty is carried out in the hospital setting under general anesthesia. Patients are admitted overnight after the procedure and discharged home the next day. Discomfort is controlled with the help of pain medications. Patients are not confined to bed and are able to carry out daily activities like showering from the next day. Most patients resume work in a week. Strenuous activities can be started after a month. Benefits of reduction mammaplasty are physical, emotional and social. After reduction mammaplasty, individuals report the absence of back and skin symptoms. Patients find it easier to perform strenuous activities. Patients have increased levels of self-confidence and are no longer embarrassed by this condition. For more information, visit us at: https://www.amicusclinic.in/breast-reduction |
AuthorI like to keep it simple. CategoriesArchives
March 2024
Categories |
- Home
-
Cosmetic
- Fat grafting
- Swellings and moles
- Scar revision
- Leukoderma (Melanocyte transfer)
- Hair transplant
- Facial rejuvenation procedures
- Nose job (Rhinoplasty)
- Cleft lip nose correction
- Ear (Otoplasty)
- Lip reduction
- Breast augmentation
- Breast reduction
- Tuberous breasts
- Axillary breasts
- Gynecomastia
- Liposuction
- Brachioplasty (Arm contouring)
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy tuck)
- Female genital rejuvenation
-
Reconstructive
- Contact
- Blog
- Home
-
Cosmetic
- Fat grafting
- Swellings and moles
- Scar revision
- Leukoderma (Melanocyte transfer)
- Hair transplant
- Facial rejuvenation procedures
- Nose job (Rhinoplasty)
- Cleft lip nose correction
- Ear (Otoplasty)
- Lip reduction
- Breast augmentation
- Breast reduction
- Tuberous breasts
- Axillary breasts
- Gynecomastia
- Liposuction
- Brachioplasty (Arm contouring)
- Abdominoplasty (Tummy tuck)
- Female genital rejuvenation
-
Reconstructive
- Contact
- Blog
You can leave us a comment using the contact form below.
We shall get back to you at the earliest.
We shall get back to you at the earliest.
Links
- Face procedures | Rhinoplasty, Otoplasty, Lip reduction, Fat grafting
- Body procedures | Gynecomastia , Breast reduction, Abdominoplasty, Brachioplasty, Liposuction
- Skin procedures | Scar revision, Moles, Leukoderma surgery
Let's be friends !
Follow us at Facebook and Twitter.
Follow us at Facebook and Twitter.
Vectors designed by Freepik
© 2024 Amicus Clinic (Plastic Surgery Centre, Trivandrum). All rights reserved.
© 2024 Amicus Clinic (Plastic Surgery Centre, Trivandrum). All rights reserved.
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed



